
The Union node takes the union of items found in two Sets, assigning the union to a Resultant Set, with the result containing items found in both Set A and Set B. Visually, the intersection of Set A and Set B looks like the following diagram, where the intersection of Set A and Set B contains items that are common to both Sets.
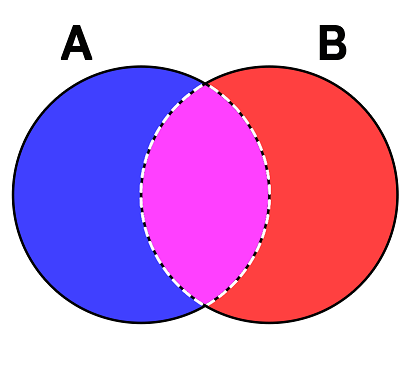
For illustrative purposes, let's say that you have two string type Sets, Set A and Set B, both of which are defined below.
Set A = {"Item 1", "Item 2", "Item 3", "Item 4", "Item 5"}
Set B = {"Item 4", "Item 5", "Item 6", "Item 7", "Item 8"}
The following table shows you the result, which contains the union of Set A and Set B (symbolically represented as A ∪ B).
| Set A | Set B | Resultant Set (A ∪ B) |
Item 1 |
Item 4 |
Item 1 |
Item 2 |
Item 5 |
Item 2 |
Item 3 |
Item 6 |
Item 3 |
Item 4 |
Item 7 |
Item 4 |
Item 5 |
Item 8 |
Item 5 |
Item 6 |
||
Item 7 |
||
Item 8 |
A Set is a collection of unique items, which means that duplicate items will be eliminated from the Resultant Set.
Inputs
| Pin Location | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
 |
(In) Exec | Input execution pin. |
 |
A | One Set to union. |
 |
B | The other Set to union. |
Outputs
| Pin Location | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
 |
(Out) Exec | Output execution pin. |
 |
Result | The Set containing the resultant union. |
Example Usage
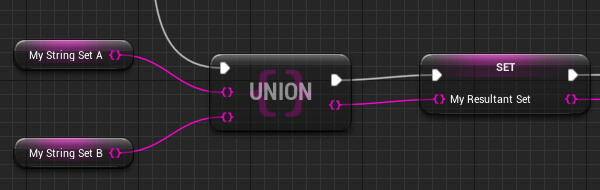
Footnote
Symbolically, this operation is represented as A ∪ B = { x | x ∈ A ∨ x ∈ B }, wherein this node is performing a logical OR operation between elements in Set A and elements in Set B.