Overview
The Virtual Camera Component (VCamComponent) is the base component that enables building custom virtual cameras in Unreal Engine.
With the VCamComponent, a user can drive a Cine Camera inside Unreal Engine by adding custom Modifiers and Output Providers.
Goals
This Quick Start guide is designed to take you through the basic steps of creating a virtual camera using the Virtual Camera Component.
Objectives
After going through this guide, you will learn the following:
- How to place a camera in the scene and add the VCamComponent.
- How to add Modifiers to the camera to customize its behaviors.
- How to add basic key inputs to enable and disable Modifiers.
- How to use different Output Providers.
1 - Required Setup
Before you start, you need to enable the appropriate plugins inside your project.
-
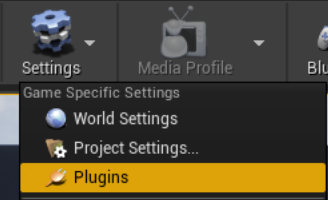
Click on Settings > Plugins to open the Plugins menu.
-
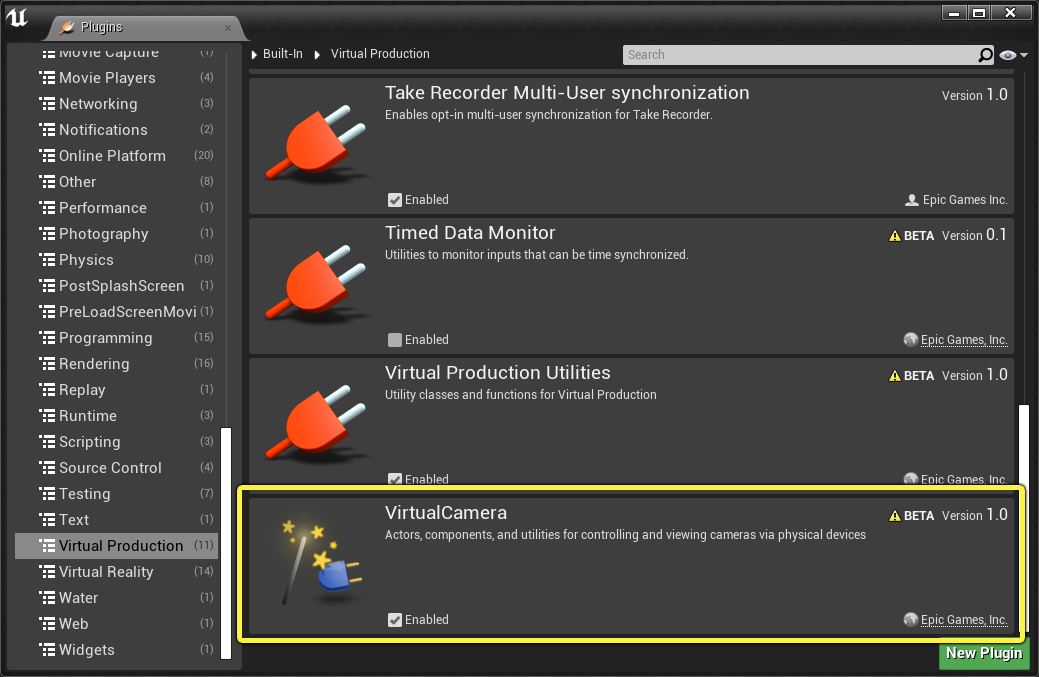
Search for the Virtual Camera plugin and enable it.
-
Restart the editor.
Section Results
You are now ready to start creating your virtual camera.
2- Creating a Virtual Camera
The Virtual Camera Component works with any Actor that contains a Cine Camera Component. In this example we will be using the Cine Camera Actor for convenience.
-
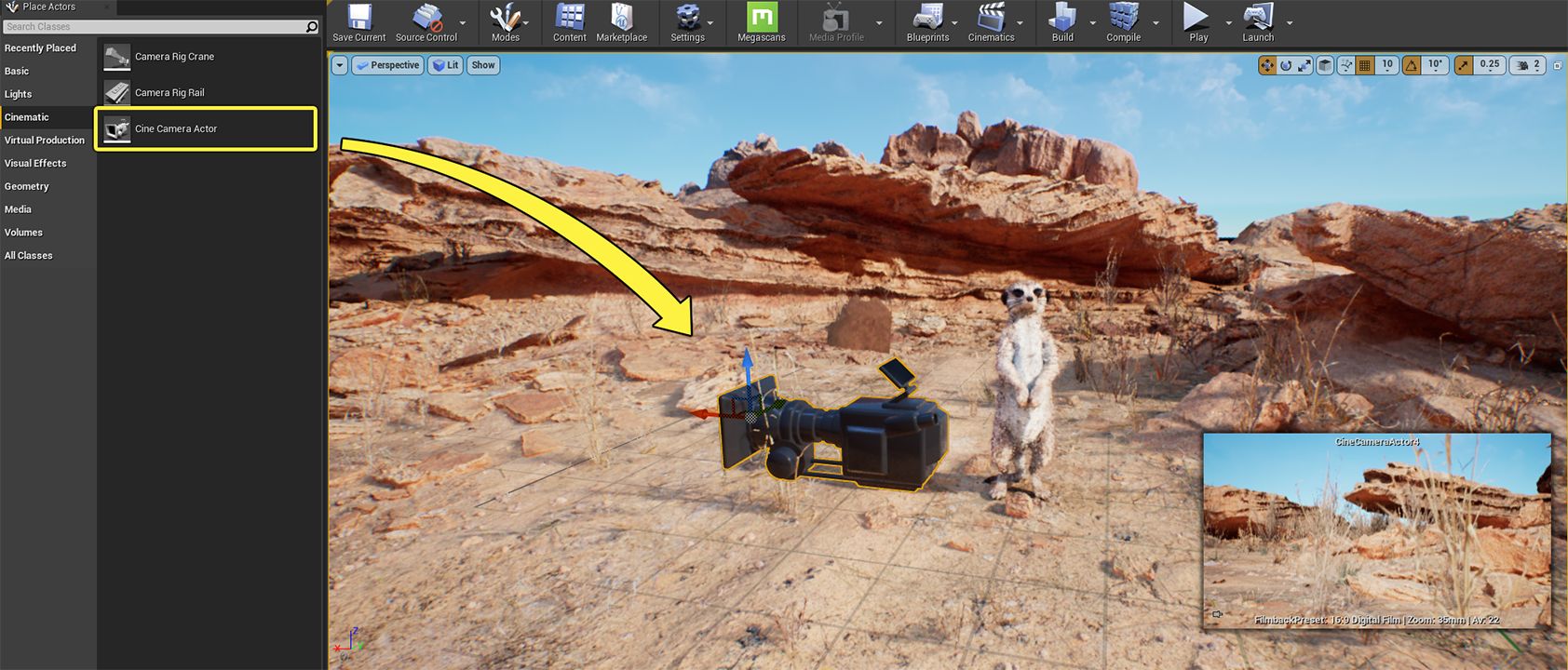
On the Place Actors panel, select the Cinematic category and click and drag the Cine Camera Actor to your scene.
-
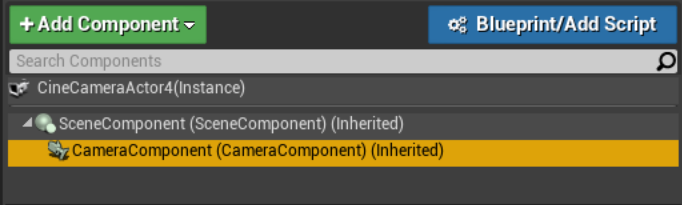
With the Cine Camera Actor selected, go to the Details panel and select the CameraComponent.
-
Click the Add Component button and search for and add the VCam component.
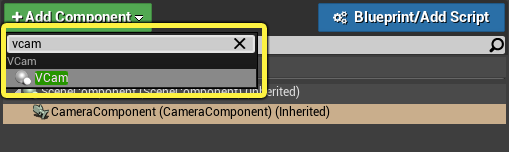
Make sure the VCam component is a child of the CameraComponent.
-
Select and click VCam to add the component.
-
Feel free to move the Cine Camera Actor in your scene and adjust the Current Camera Settings to your liking. In the example below, we moved the camera to frame the meerkat in the scene and adjusted the camera to always keep the subject in focus.
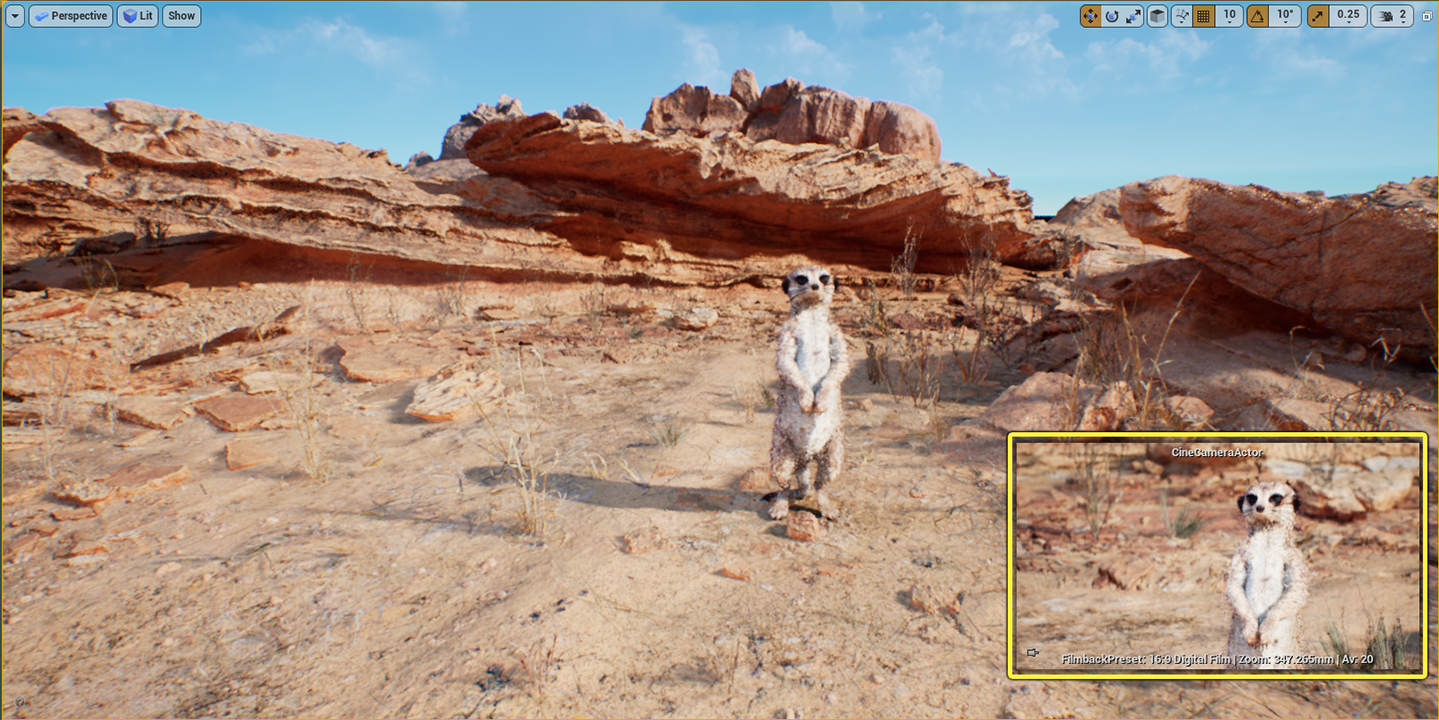

You can learn more about adjusting the camera settings by going to the Cine Camera Actor documentation page.
-
Select the Camera Actor, then select the VCam component in the component hierarchy.
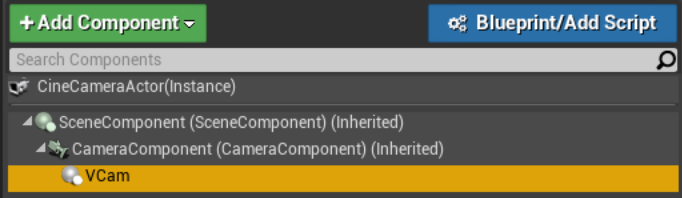
-
You can now see the properties available under the Virtual Camera section.
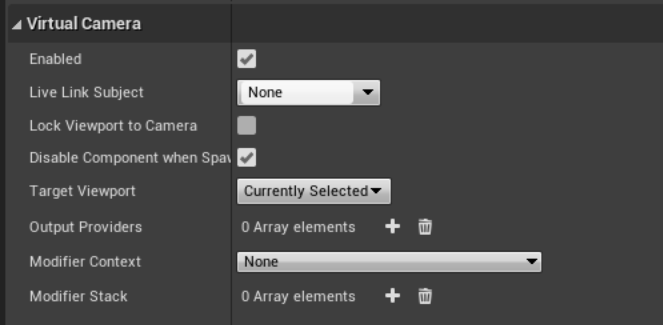
The properties are as follows:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Enabled | This toggle enables and disables the entire Virtual Camera Component. |
| Live Link Subject | This is the subject used via the Live Link plugin. The component uses the subject’s camera information to drive the camera in the scene. |
| Lock Viewport to Camera | The viewport will be rendered from the point of view of the virtual camera. |
| Disable Component when Spawned by Sequencer | Disables the Virtual Camera Component when spawned by a Sequence. This prevents a situation where two VCam components might become active at the same time when you play a Sequence that contains a VCam component set as spawnable. |
| Target Viewport | This is the editor viewport that will be used by the component to render its view. |
| Output Providers | Contains a list of all output device destinations. |
| Modifier Context | An optional object that contains arbitrary data that is shared between all Modifiers. |
| Modifier Stack | Contains a list of all Modifiers added to the component. |
Section Results
You placed a Cine Camera Actor in your scene and added the Virtual Camera Component. You are now ready to customize your camera by adding Modifiers.
3 - Adding Modifiers
Modifiers can manipulate the camera by adding custom effects and behaviors to simulate real life camera behaviors. You can create custom modifiers with Blueprints or C++ and add them to the stack to layer different effects.
The Modifiers in the stack will be executed from top to bottom and the effects will be applied in that order.
Creating your First Modifier
-
Right-click inside the Content Browser and select the VCam Modifier under the Virtual Camera category.
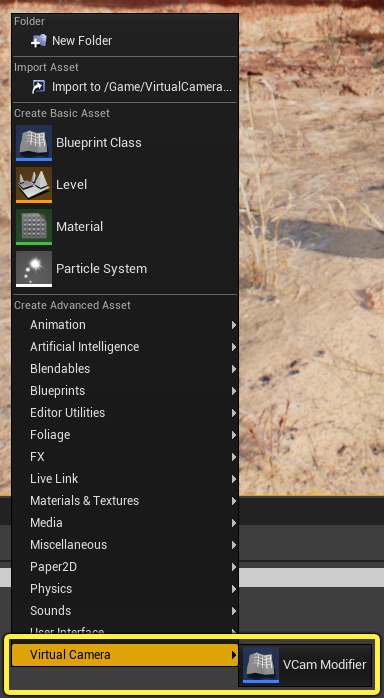
-
Name your Blueprint VCM_LookAt, then double-click it to open it.
-
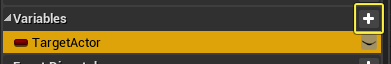
Go to the My Blueprint tab and click on the plus sign next to Variables to add a new variable. Name the new variable TargetActor.
-
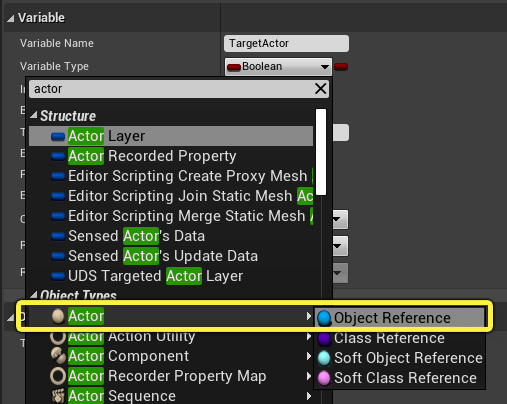
With TargetActor selected, go to the Details panel and click on the Variable Type dropdown. Search for Actor and select the Object Reference.
-
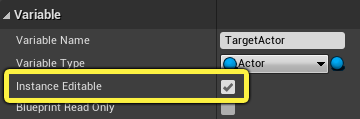
Select the Instance Editable checkbox and Compile and Save the Blueprint.
-
Drag TargetActor into the Event Graph and select Get TargetActor. Then drag from the node and search for and select Is Valid, as shown below.
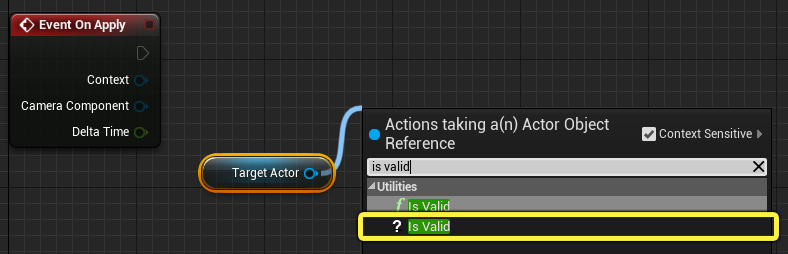
-
Connect the Event on Apply node to the Is Valid node.
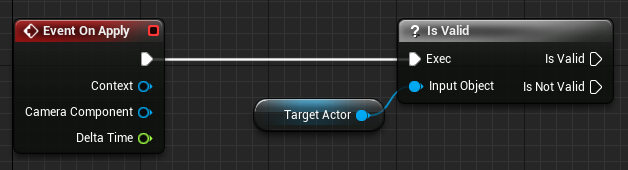
-
Drag from the Camera Component pin of the Event On Apply node and search for and select Get World Location.
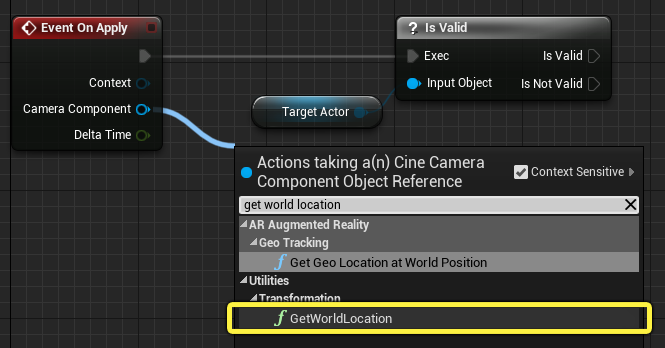
-
Drag from TargetActor and search for and select Get Actor Location.
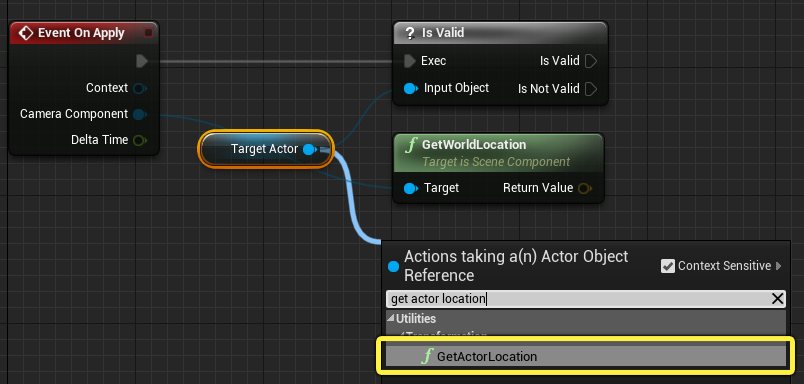
-
Drag from the Return Value of the GetWorldLocation node and search for and select Find Look At Rotation.
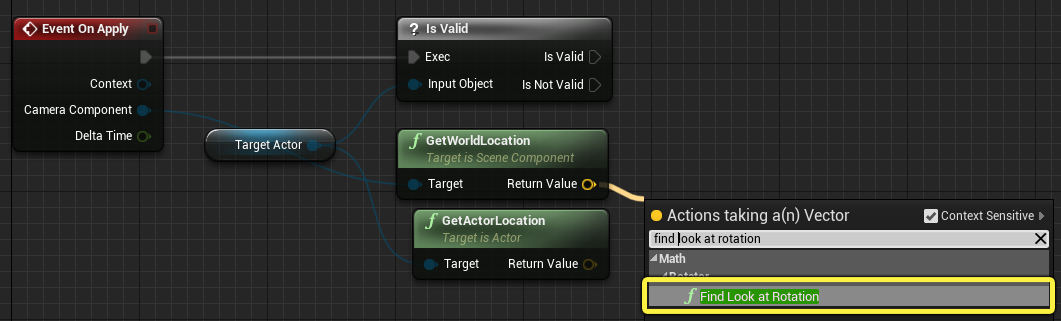
-
Connect the Return Value pin of the Get Actor Location node to the Target pin of the Find Look at Rotation node.
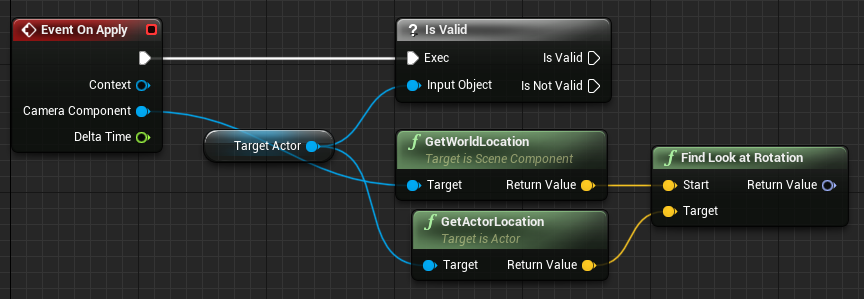
-
Drag from the Camera Component pin of the Event On Apply node and search for and select Set World Rotation.
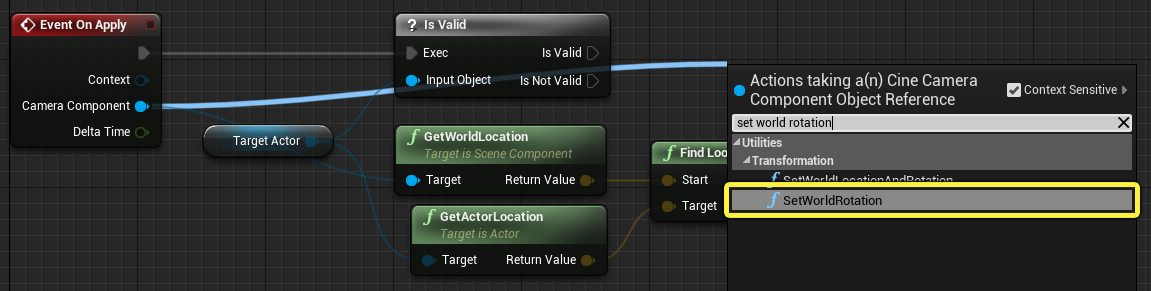
-
Connect the Is Valid pin from the Is Valid node to the Set World Rotation node. Connect the Return Value pin of the Find Look at Rotation node to the New Rotation pin of the Set World Rotation node.
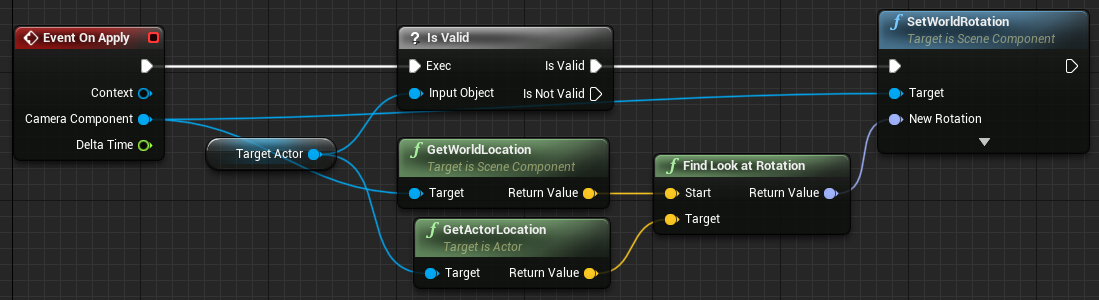
-
Compile and Save the Blueprint.
Adding the Modifier to the Stack
Now you are ready to add your custom Modifier to the Modifier Stack.
-
Go to the Place Actors tab and under the Basic category, click and drag a Sphere into the level.
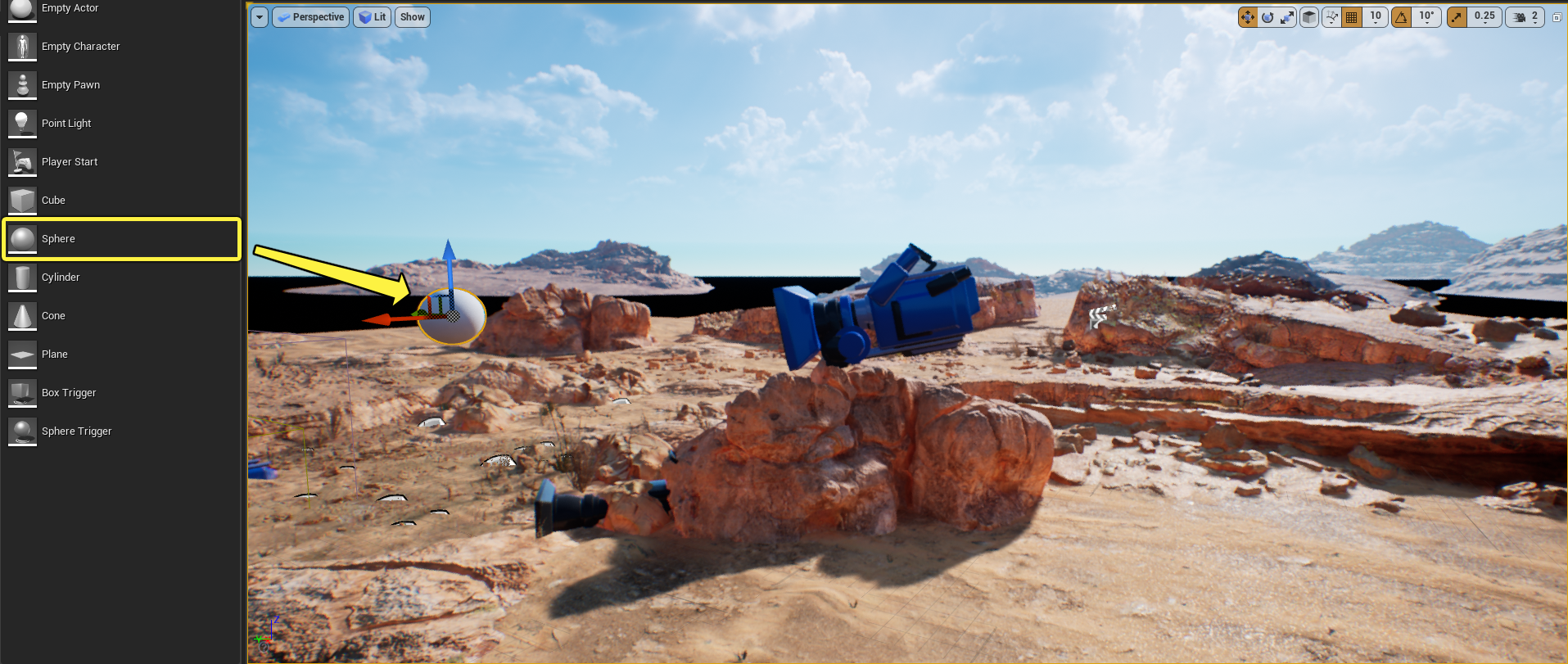

-
Select your Camera Actor and inside the component hierarchy, select the VCam component.
-
Click the plus sign on the Modifier Stack to add an entry to the list.
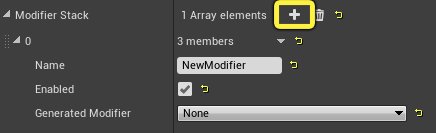
-
Enter a name for your Modifier, such as Look At. Adding a name allows you to reference this Modifier in your Blueprints later on.
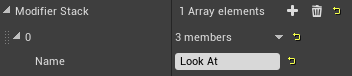
-
Click on the dropdown arrow for Generated Modifier and select VCM_LookAt from the list.
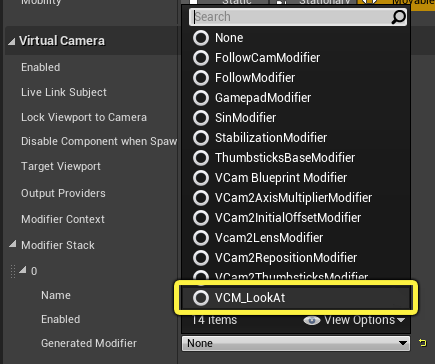
-
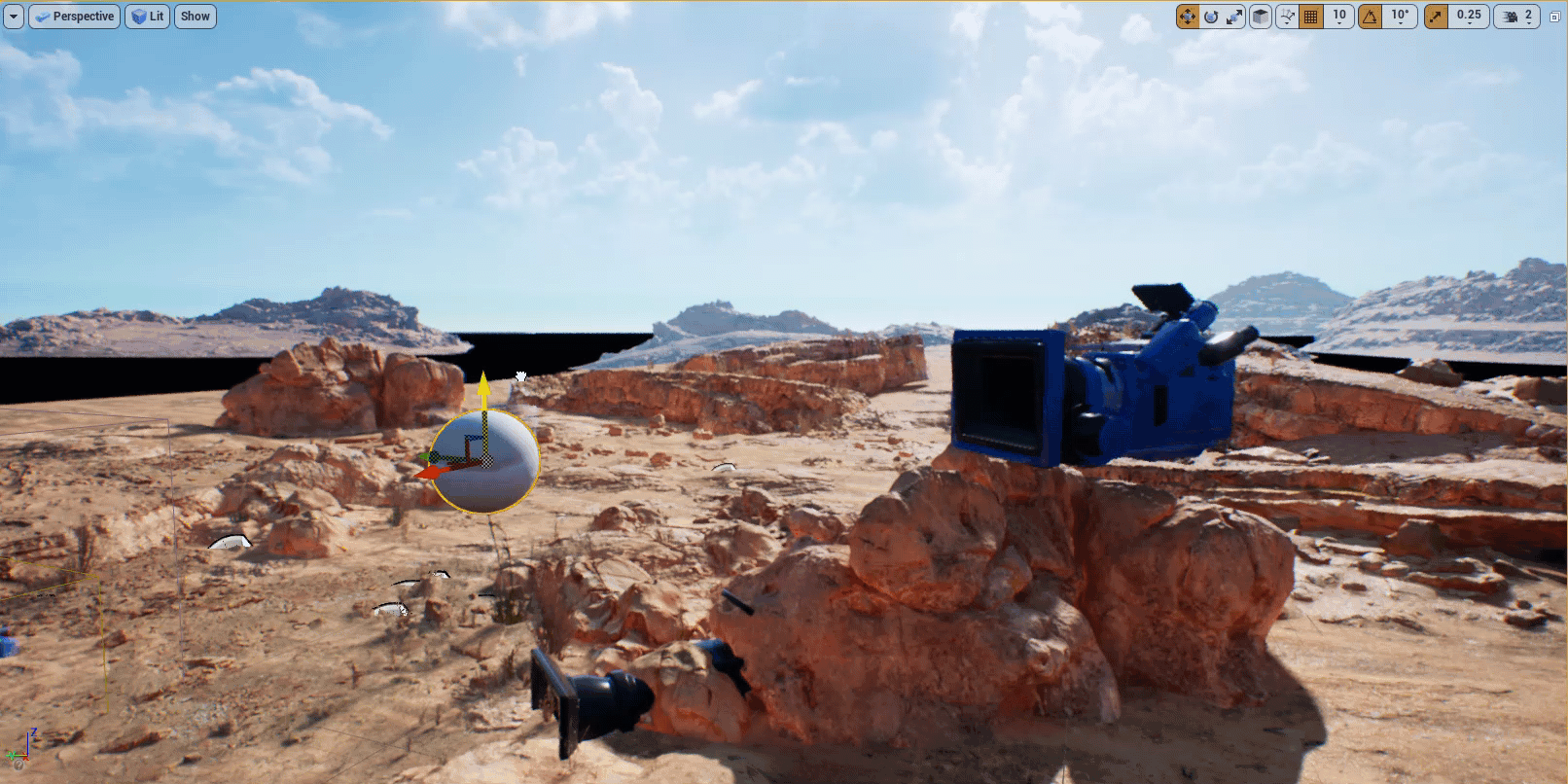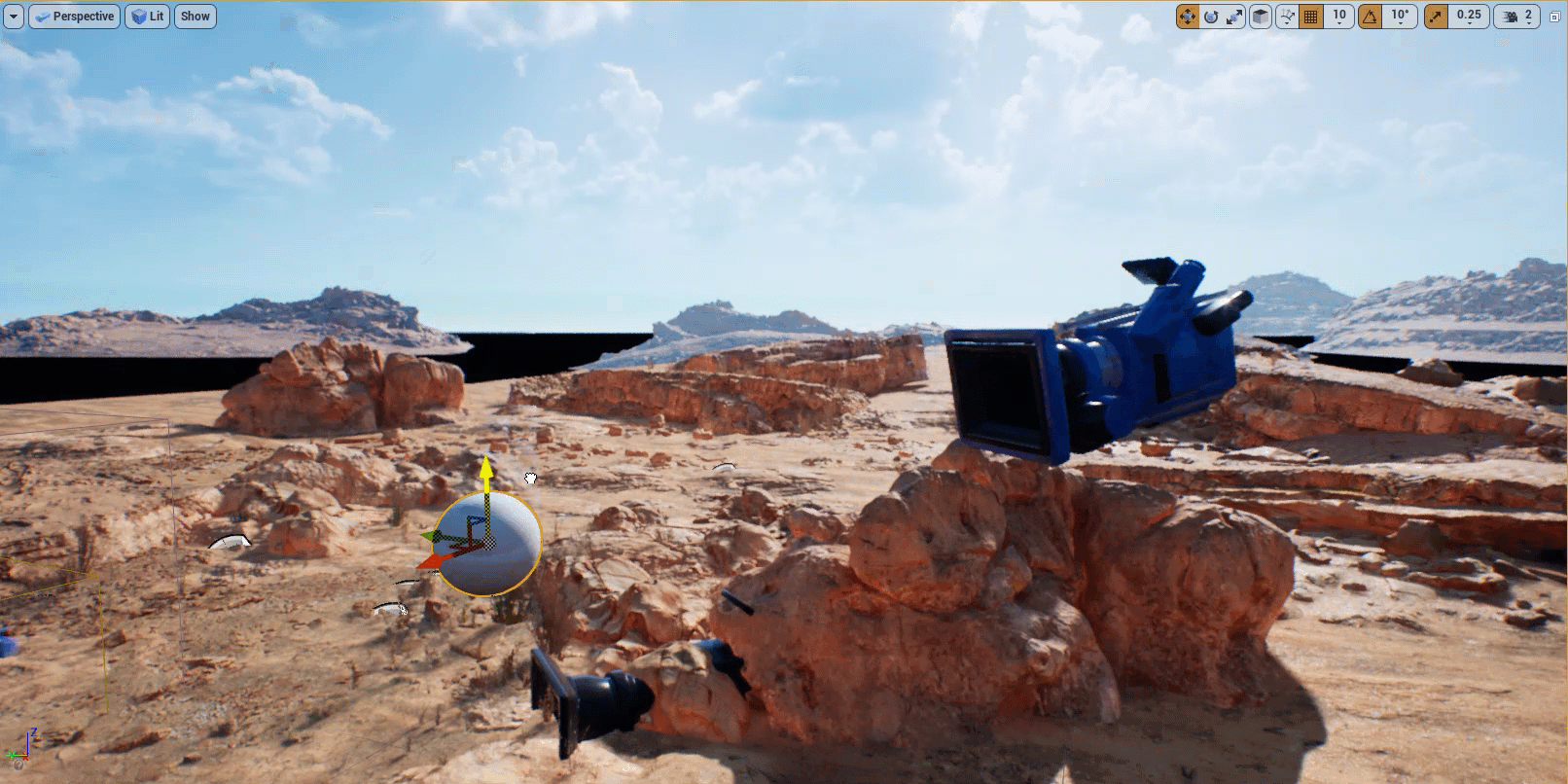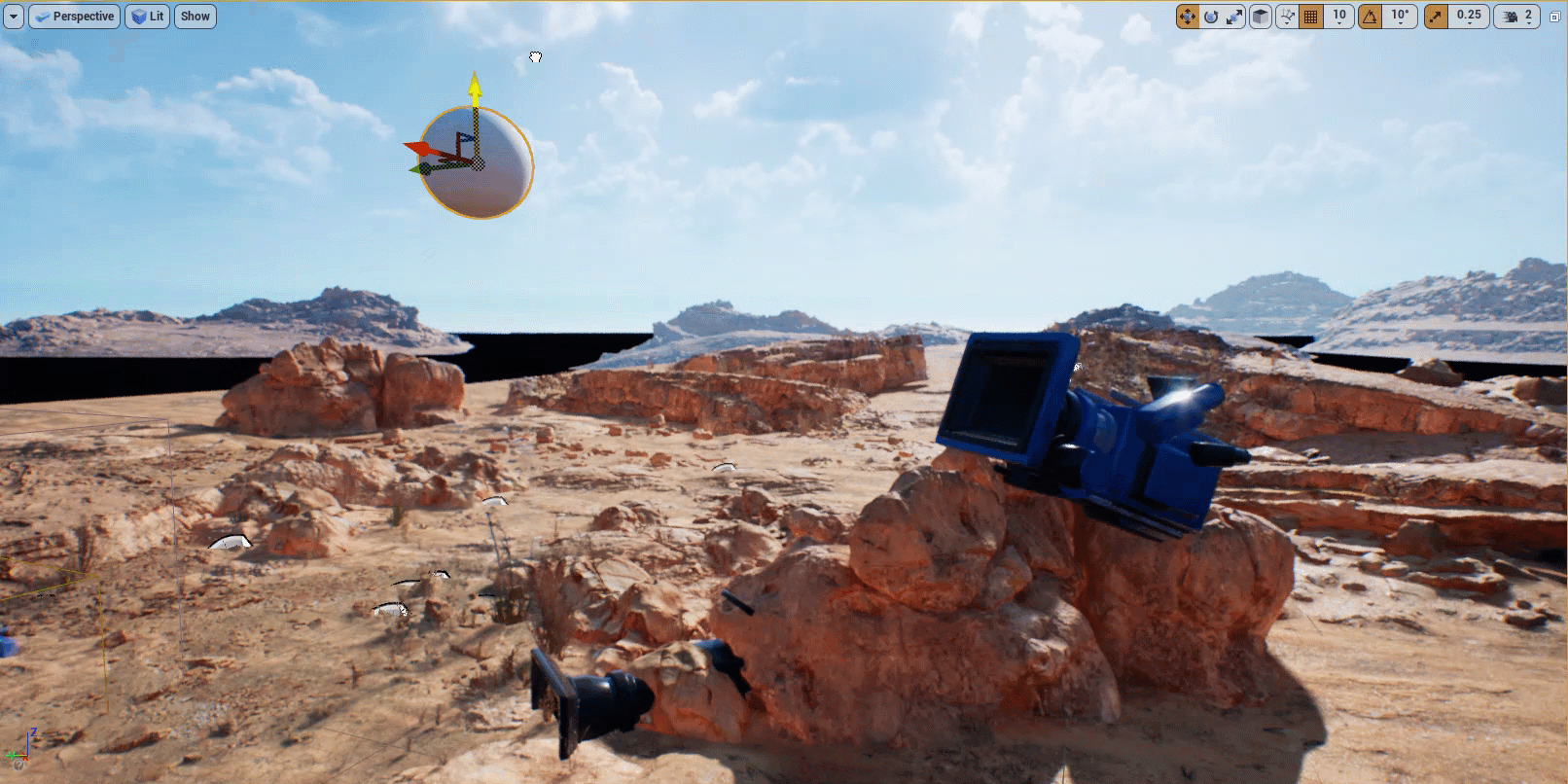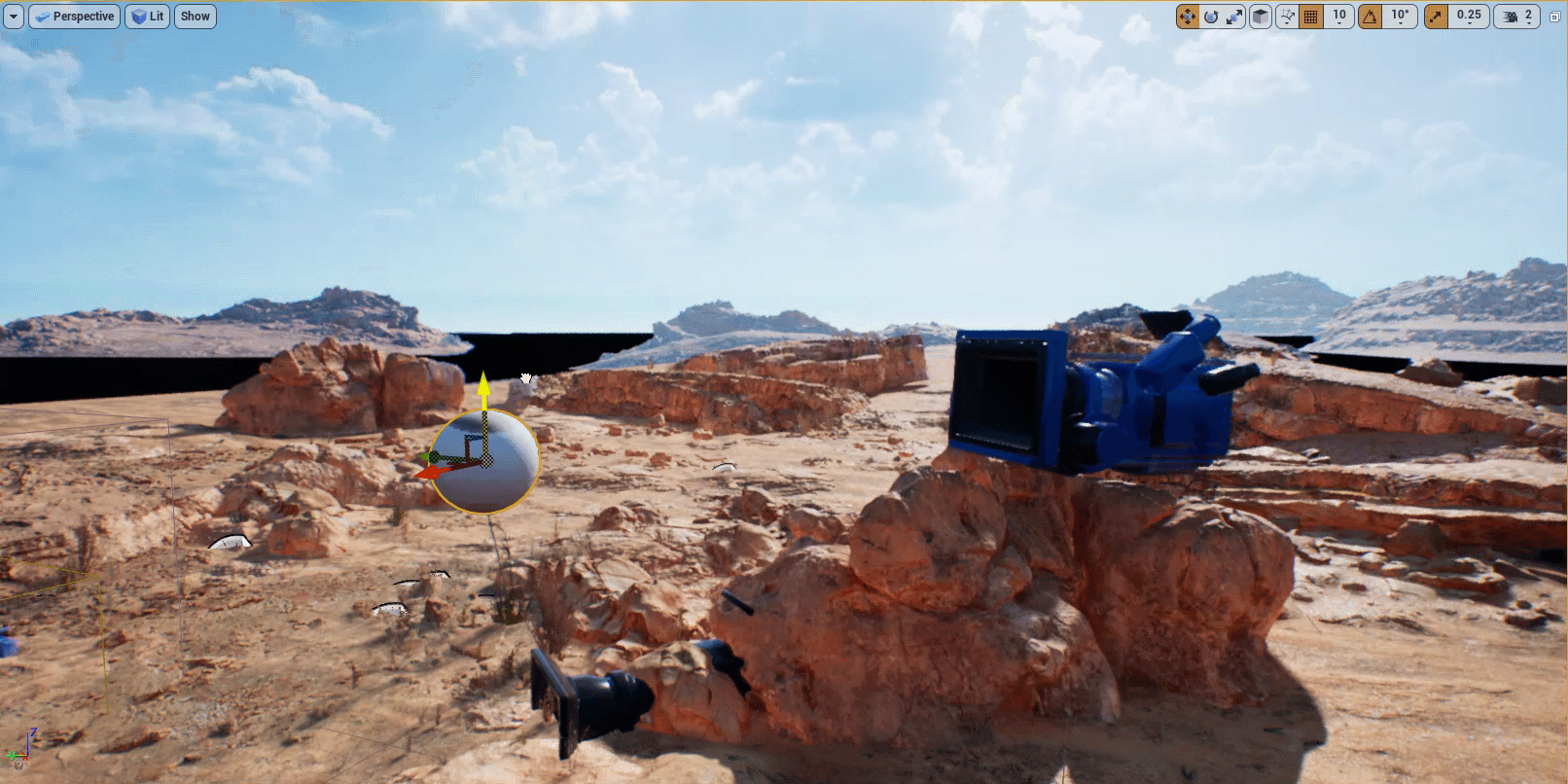
Expand the Default section of the Modifier and click on the Target Actor dropdown. Select the Sphere Actor you added to the level.
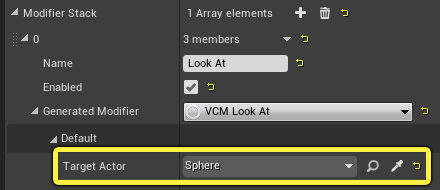
-
Select the Sphere Actor in your level and move it. You will see the camera rotate towards the Sphere.
Section Results
In this section you learned how to create a custom camera modifier by using Blueprints.
You also learned how to add your custom modifier to the Modifier Stack to manipulate your virtual camera inside the editor.
4 - Using the Virtual Camera Input System
The current Virtual Camera input system is a placeholder and will be replaced by a more advanced version in the future.
The Virtual Camera Component can use Editor Input Events directly inside Modifiers to provide additional control to the user.
Here is how you can use this system to add additional functionality to your Modifier.
Goals
Our goal for this section will be to add a key input to our Modifier that will allow us to enable and disable the effect by pressing a single key.
Creating an Input Event
-
Open the VCM_LookAt Blueprint by double clicking it in the Content Browser.
-
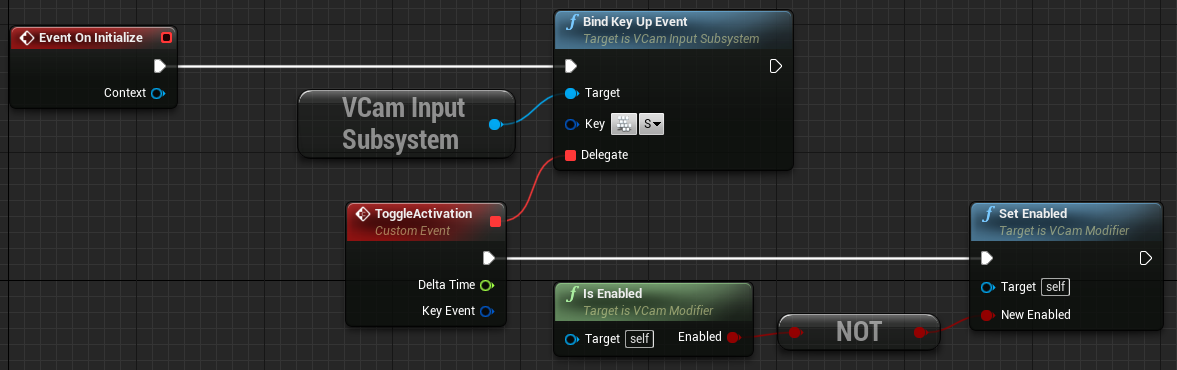
Right click on the Event Graph then search for and select the function Get VCamInputSubsystem.
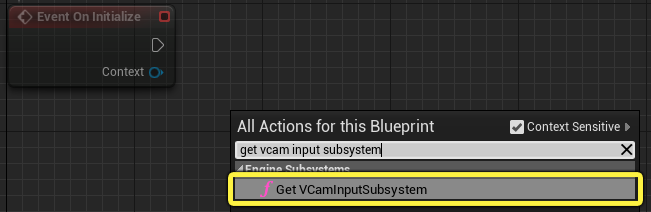
-
Drag from the VCam Input Subsystem node then search for and select the Bind Key Up Event. Connect the Event On Initialize node with the Bind Key Up Event node.
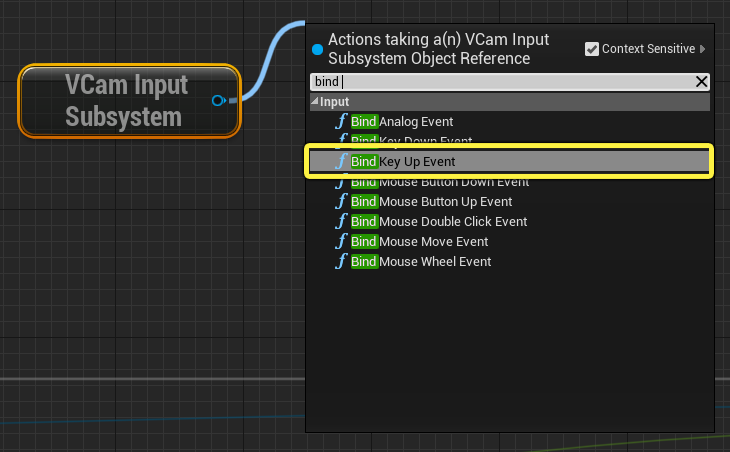
-
Drag from the red Delegate pin and search for and select Add Custom Event. Name the new custom event ToggleActivation.
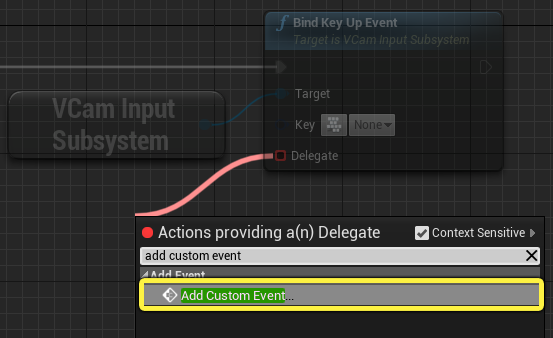
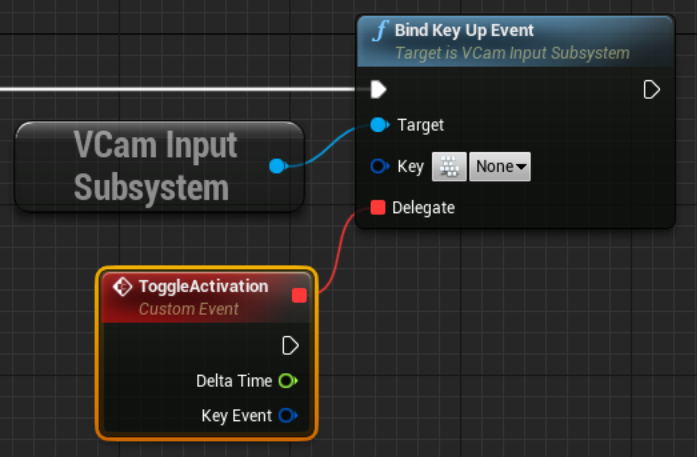
-
On the Bind Key Up Event node, click on the keyboard icon and press the S key to bind it to the event. Alternatively, you can press the dropdown arrow and select the desired key from the list.
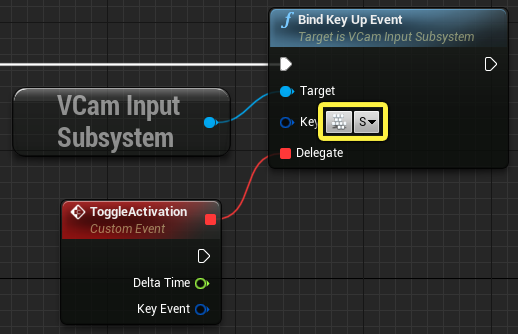
-
Right click on the Event Graph and search for and select Set Enabled under the Virtual Camera category. Connect the ToggleActivation node to the Set Enabled node.
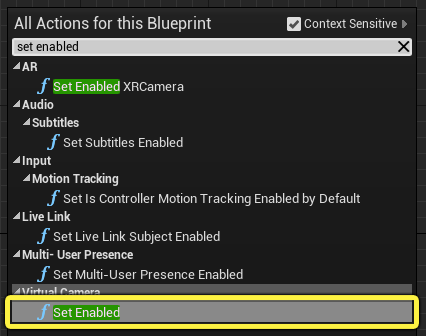
-
Right click on the Event Graph and search for and select Is Enabled under the Virtual Camera category.
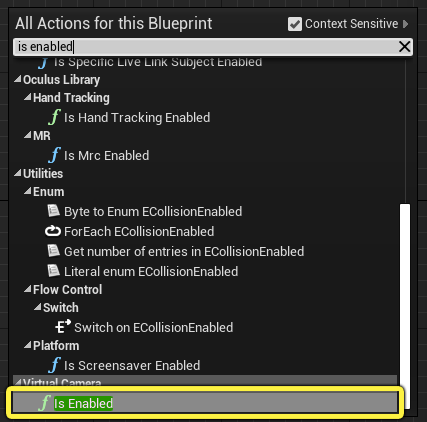
-
Drag from the Is Enabled node and search for and select Not.
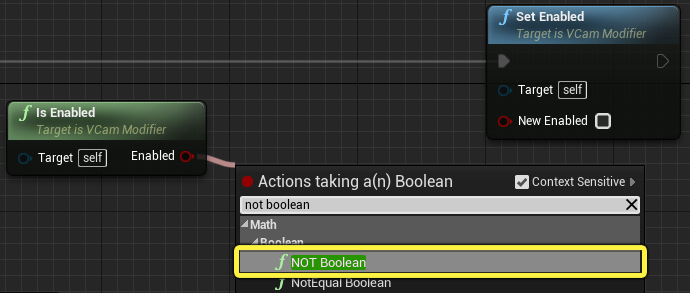
-
Connect the Not node to the New Enabled pin of the Set Enabled node.
-
Return to your scene and while moving the Sphere Actor in the level, press S to toggle the effect on and off.
The virtual camera input system executes every time the user presses a key, even when the viewport is not in focus. This can cause conflicts when the user presses the key for other purposes. For example, if the user renames an asset in the Content Browser and uses the letter S, it will execute your event.
-
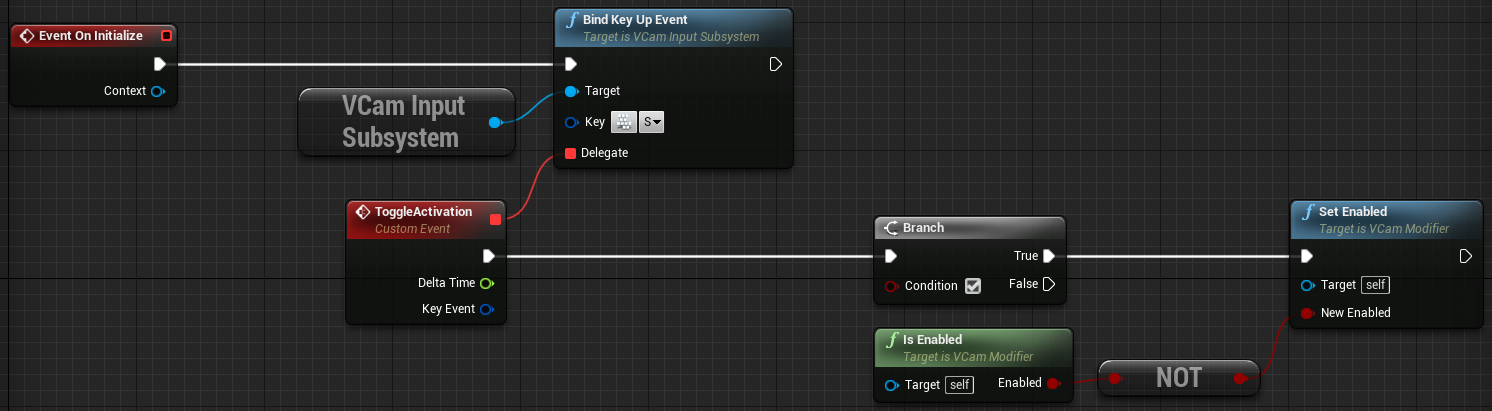
To prevent accidental activation of the Modifier, you can add an additional safeguard to your code such as adding the Shift key as part of the input.
-
Go back to VCM_LookAt and add a Branch node between the ToggleActivation event and the Set Enabled node, as shown below.
-
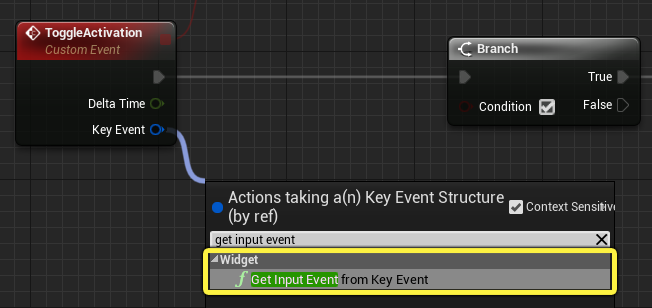
Drag from the Key Event pin of the Toggle Activation node, then search for and select the Get Input from Key Event function.
-
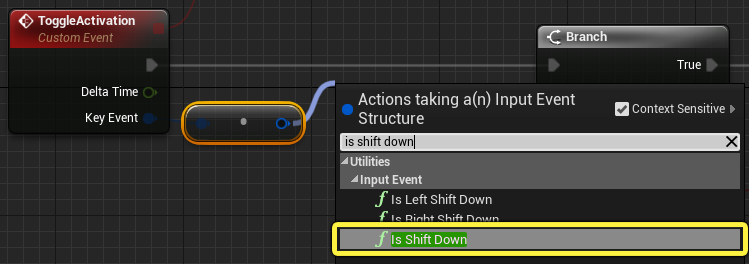
Drag from the node, then search for and select the Is Shift Down function.
-
Finally, connect the Is Shift Down node to the Condition pin of the Branch node, as seen below.
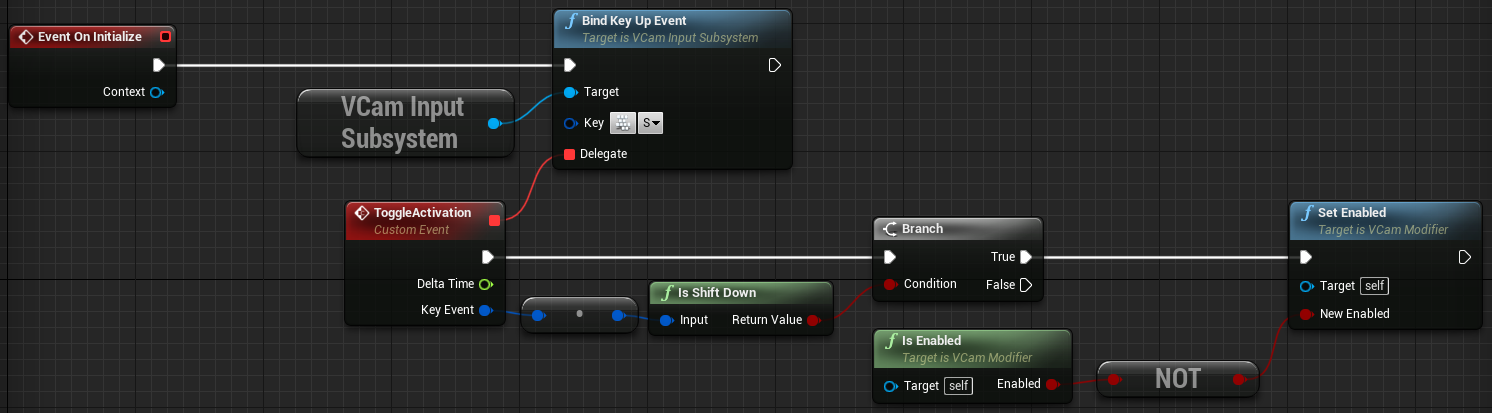
-
Your Modifier will now execute only when the Shift key is down and you press the S key.
Section Results
In this section you added an input event that executes when the S key is pressed. This event enables and disables the effect of your Modifier. In addition, you added the Shift key as a safeguard to prevent conflicts when the user presses the S key for another purpose.
5 - Adding Output Providers
The Output Provider system is used to route the output of the virtual camera onto various providers including viewports, devices using the remote session protocol, the Composure plugin, and various supported video capture cards.
The Output Providers list is always executed in order, starting from the top.
Let's take a look at the available Output Providers that come with the Virtual Camera Component.
Viewport Output Provider
This Provider will output the virtual camera’s view directly to the main viewport in the editor.
-
Select the VCam component and click on the + sign next to the Output Providers to add a new Provider to the list.
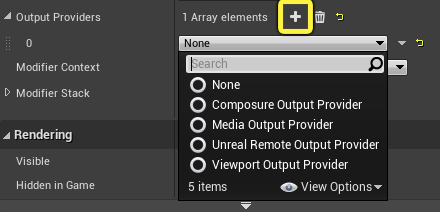
-
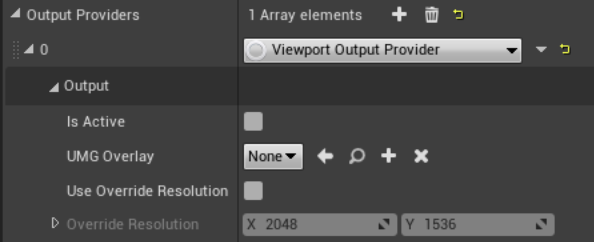
Select the Viewport Output Provider option from the list.
-
You can now see the shared properties among the different Providers:
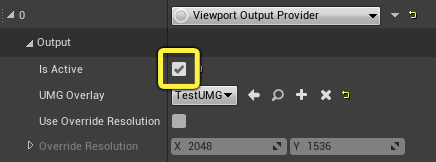
Property Description Is Active Enables and disables the Provider. UMG Overlay UMG widget that is overlaid on top of the image output. Use Override Resolution Sets a custom resolution to the output image. This is especially useful when using external devices with fixed resolutions. Override Resolution This is the fixed resolution used for the output image. -
As an example, click on the UMG Overlay dropdown and search for and select TestUMG to add a test widget to the viewport.
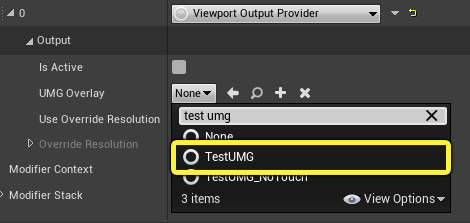
-
Finally, set the Output Provider as Active by clicking on the checkbox.
-
You should now see an overlay on the main viewport in your scene.This is an example of how you can customize your camera output to fit your specific needs.
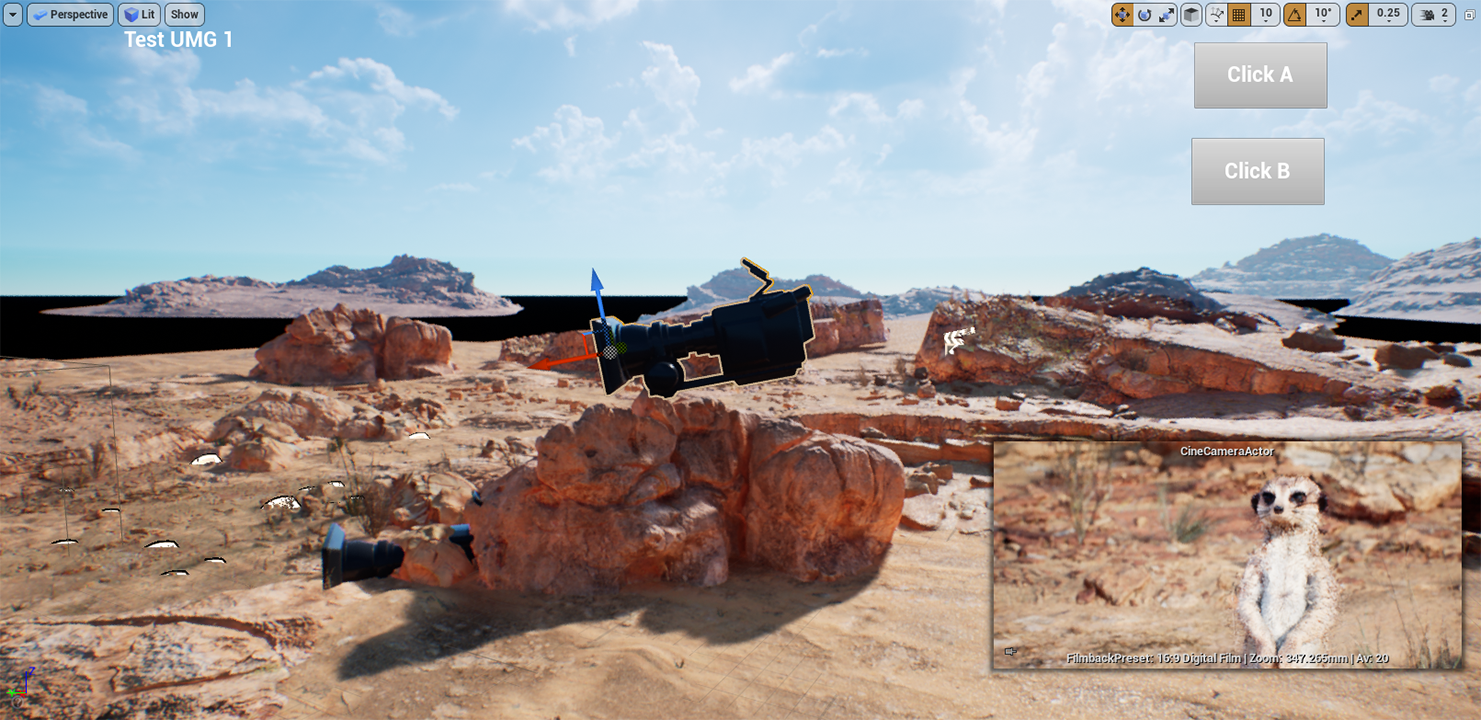

Unreal Remote Output Provider
This Provider outputs the main editor viewport to a remote device connected via the Remote Session protocol, such as the Unreal Remote 2 app. Any compatible device connected with this method can be used for this purpose.
Next you will configure your project to connect an external device using Remote Session.
-
Open Settings > Project Settings.
-
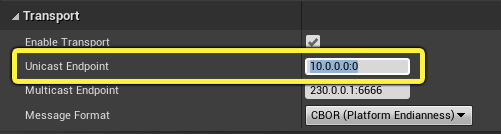
Go to the UDP Message section and set your Unicast Endpoint to your computer’s IP address with :0 at the end of the IP to indicate your port number.
-
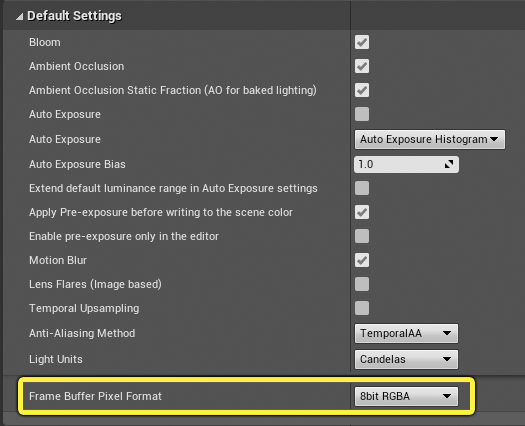
Go to the Rendering section and under Default Settings click on the arrow to expand the advanced settings. Set your Frame Buffer Pixel Format to 8bit RGBA.
-
Restart the editor.
iOS Device Setup
Download the VCAM App from the App Store to your ARKit enabled iOS device and launch the app.
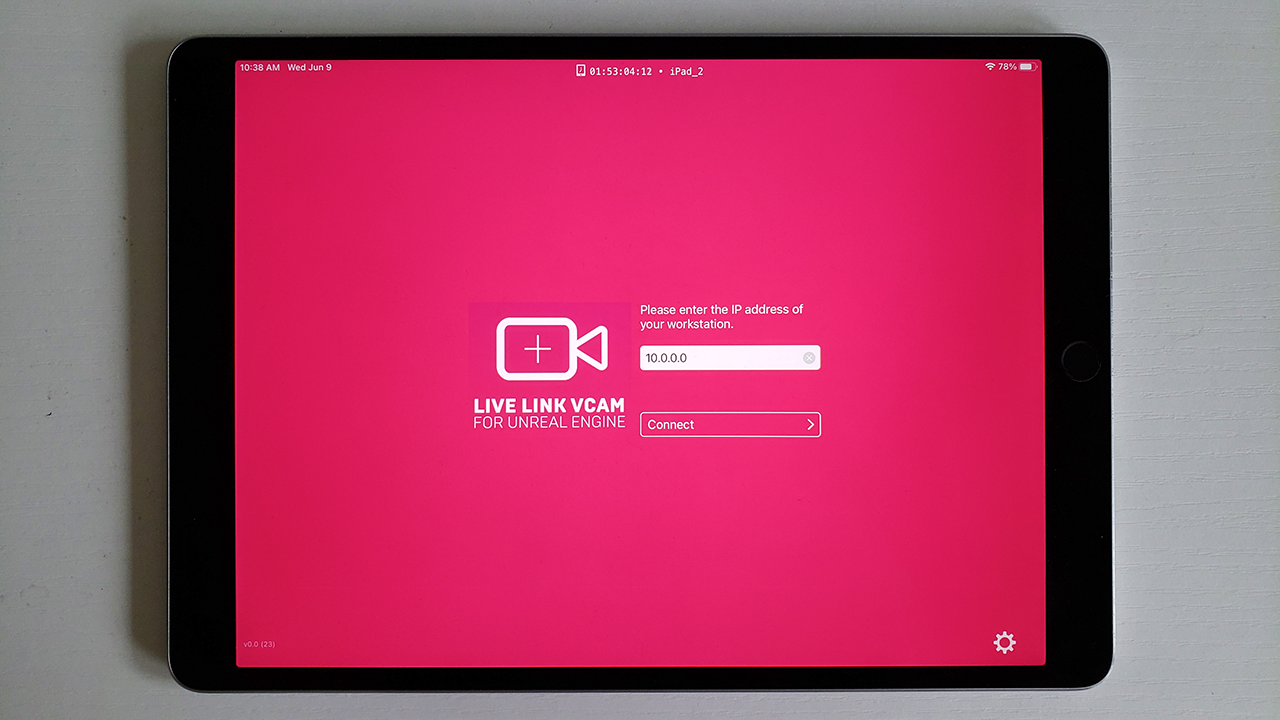
Connecting your device
-
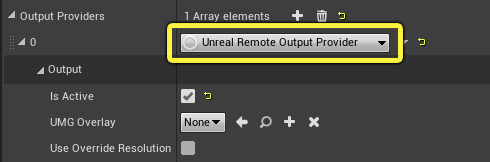
Select the VCam component on your virtual camera actor, and select the Unreal Remote Output Provider from the Output Provider dropdown list.
-
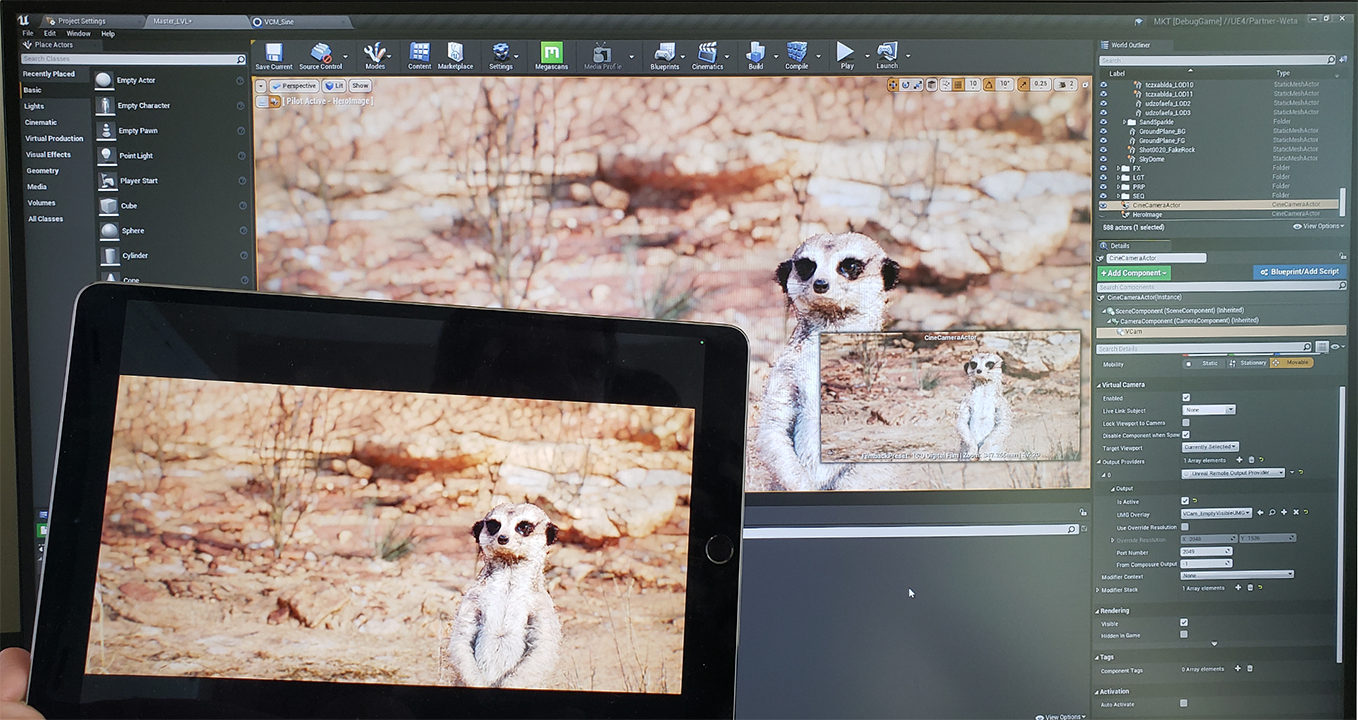
Open the Unreal Remote 2 app on your device. Enter the IP address of your computer and tap the Connect button to try and establish a connection.
-
You should now see the main editor viewport mirrored on your device’s screen.
Media Output Provider
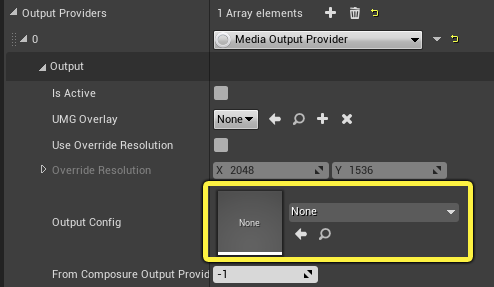
The Media Output Provider sends the virtual camera’s output to any device supported by the Unreal Media Framework, such as video capture cards from Black Magic and AJA.
Once chosen, you can select the Output Config, which is used to specify the output parameters.
For more information on how to use the Unreal Media Framework, visit the Media Framework documentation page.
Composure Output Provider
The Composure Output Provider sends the virtual camera’s output to a render target that can be used directly by the Composure Plugin. In addition, you can specify the Composure Layer Targets that the camera’s view will be rendered on.
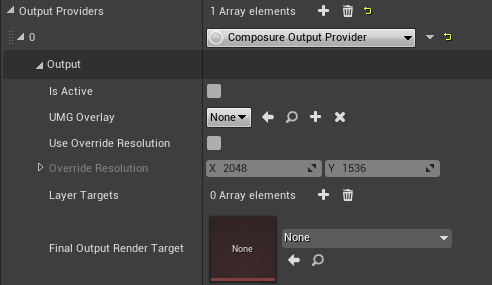
For more information on how to use the Composure Plugin, please visit the Real-Time Compositing with Composure documentation page.
Section Results
In this section you learned how to add different Output Providers to your Virtual Camera component. You can now use your virtual camera to output directly to the editor viewport, or an external device via the Remote Session protocol.
You also learned how to send your output to be processed by the Unreal Media Framework and the Composure Plugin.
Next Steps
Now that you know how to build your own virtual camera, take a look at the pre-built Virtual Camera Actor that comes included in the Unreal Engine by going to the Virtual Camera Actor Quick Start.
