Sequencer gives users the ability to create in-game cinematics through its specialized multi-track editor. By creating Level Sequences, adding tracks, and creating keyframes you can manipulate objects, characters, and cameras.
This page provides an overview of Sequencer Actors, Level Sequence Assets, and the primary features of Sequencer.
Sequencer Asset and Actor
Sequencer in Unreal Engine consists of 2 main parts: a Level Sequence Asset and a Level Sequence Actor.
The Level Sequence Asset is located in the Content Browser and contains Sequencer’s data. This includes tracks, cameras, keyframes, and animations. This is assigned to a Level Sequence Actor in order to bind its data to a Level.
The Level Sequence Actor is located in the Level and is the container for the Level Sequence Asset. You can select it to view its details in the Details panel.
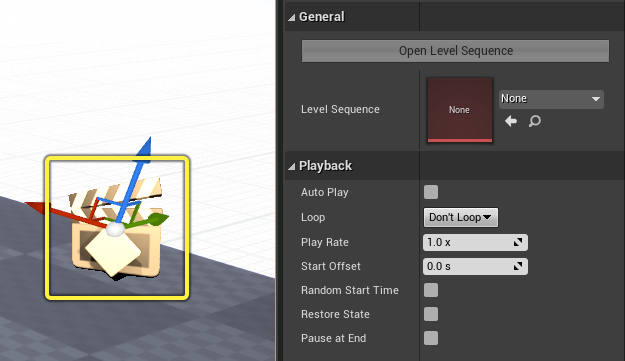
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Open Level Sequence | Opens the Sequence Editor for the currently bound level sequence asset. |
| Level Sequence | The currently bound level sequence asset. |
| Playback | |
| Auto Play | The sequence will automatically play when the actor is created. |
| Loop | Loop options for the sequence. Don’t Loop will cause the sequence to play once and finish. Loop Indefinitely will cause the sequence to loop forever. Loop Exactly... will expose a numerical time entry where you can specify the amount of times the sequence will loop, then finish. |
| Play Rate | The speed of the sequence to play. Does not affect Time Dilation. |
| Start Offset | The amount of time in seconds the sequence should start relative to the start time. |
| Random Start Time | Starts playing the sequence at a random point between the start and end time. Enabling this will disable Start Offset. |
| Restore State | Restores all actors to their previous state before the sequence started. |
| Pause at End | The sequence will pause upon reaching the end, keeping all actors in their final positions in the sequence. |
| Cinematic | |
| Disable Movement Input | Disables translation input from the player pawn for the duration of the sequence. |
| Disable Look At Input | Disables rotation input from the player pawn for the duration of the sequence. |
| Hide Player | Disables the player pawn’s visibility for the duration of the sequence. |
| Hide Hud | Hides all Heads Up Display (HUD) elements for the duration of the sequence. |
| Disable Camera Cuts | Disables the Camera Cuts track, causing the sequence to not take control of the camera. |
Sequencer Creation
There are several ways you can create and assign your Level Sequences.
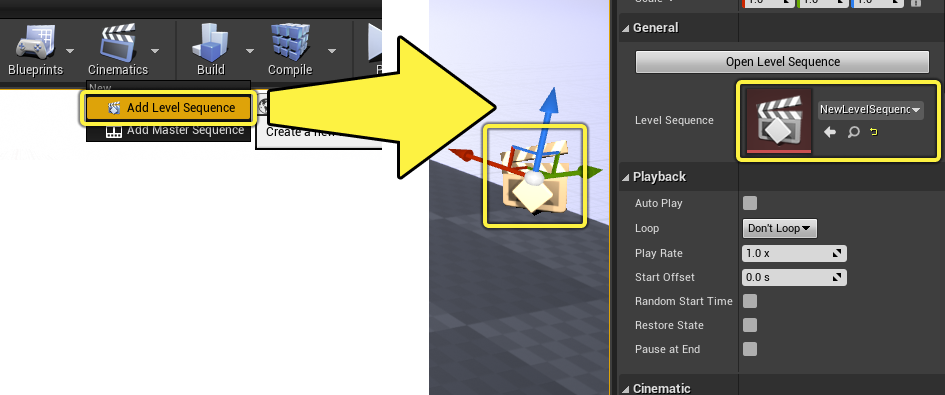
One of the quickest ways is to click the Cinematics dropdown in the Level Editor’s main toolbar and select Add Level Sequence. This will prompt you to create a new Level Sequence Asset in the Content Browser. Give it a name and click Save. Once created, your Level will now contain a Level Sequence Actor with a reference to the newly created Level Sequence Asset.
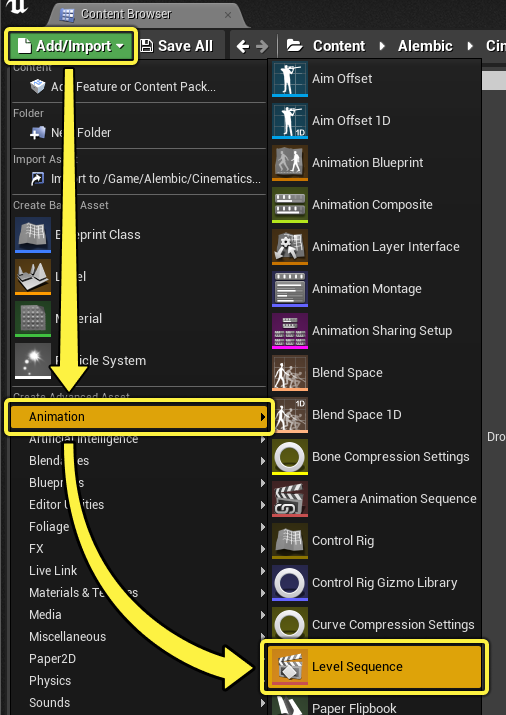
An alternate way of creating and assigning your sequence is to click Add/Import > Animation > Level Sequence in the Content Browser. This will also prompt you to create a new Level Sequence Asset.
Once the sequence Asset has been created, navigate to the Place Actors panel and drag in a Level Sequence Actor from the Cinematic category.
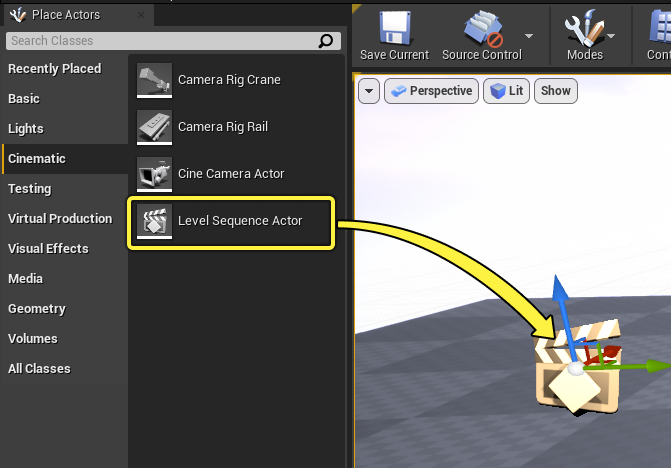
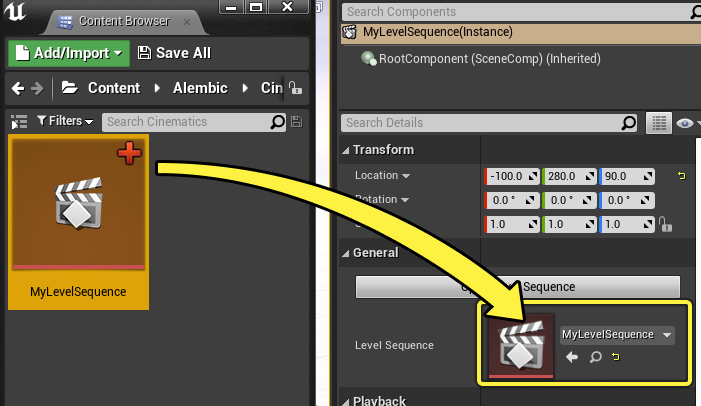
Then bind your Level Sequence Asset to the Level Sequence Actor by dragging and dropping the Asset onto the Level Sequence property.
Sequencer Editor
The Sequencer tab contains the Sequencer Editor, which provides a user interface for creating cinematic content.
There are various ways you can open this window.
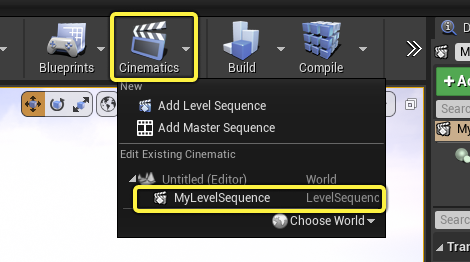
One way is to click the Cinematics dropdown in the Level Editor’s main toolbar and select your sequence from the list. Your sequence must be assigned to a Level Sequence Actor within your Level for it to appear here.
Another way is by clicking the Level Sequence Actor’s Open Level Sequence button in the Details panel.
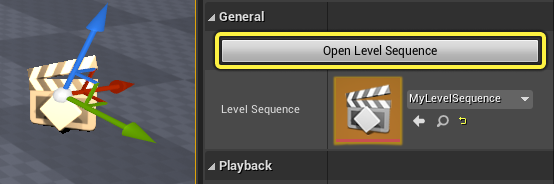
Or by double-clicking the Level Sequence property icon in the Details panel.
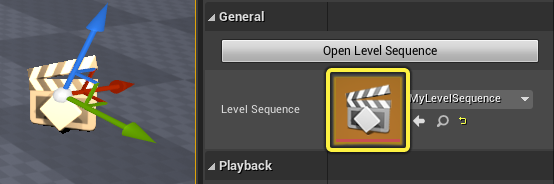
You can also open it by double-clicking the Level Sequence Asset in the Content Browser.
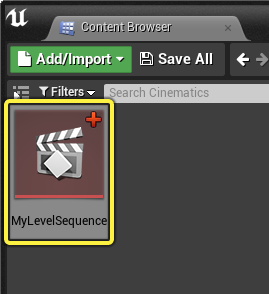
When opening a sequence from the Content Browser, you must currently have a Level opened in which this sequence is being referenced. Otherwise the contents will be unbound.
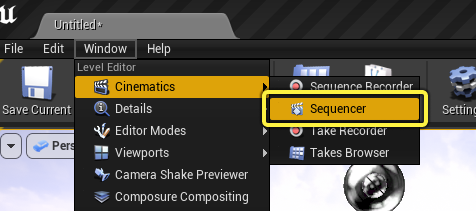
Finally, you can open it by navigating to the main menu bar and clicking Window > Cinematics > Sequencer.
Visit the Sequencer Editor Reference page for more information on the Sequencer editor.
Sequencer Tracks
Similar to other film and animation editing software, Sequencer requires you to add tracks in order to reference elements in your sequence.
Any character, prop, camera, effect, or other viewport element can be referenced and manipulated in Sequencer. Auxiliary tracks can also be added to enhance or control other aspects of a scene, such as fades, materials, or Level visibility.
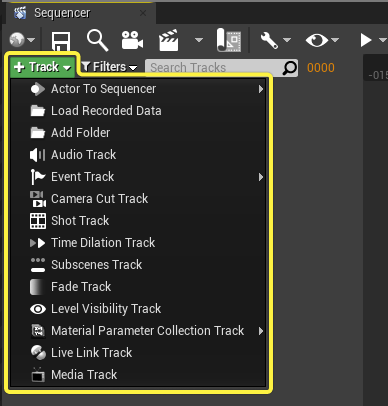
Visit the Tracks page for more information on the various tracks you can add in Sequencer.
Keyframing
The main way you will affect Actors in the scene is by creating keyframes or keys to manipulate their transforms, properties, or animations. Upon reaching a keyframe in the timeline, the track’s properties are updated to reflect the values you have defined at that point.
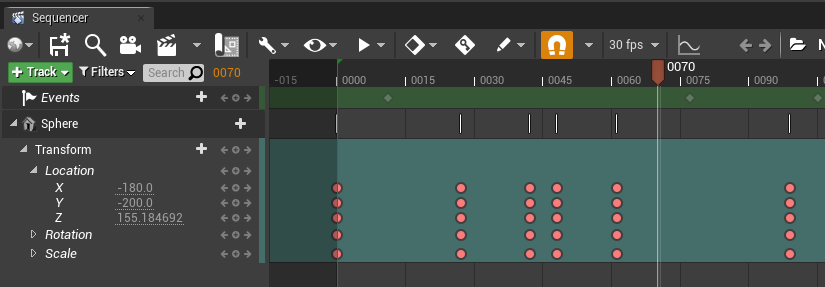
Visit the Keyframing page for further information on keyframing.
Curve Editor
You can use Sequencer’s Curve Editor to fine-tune your keyframes and the curves they generate. It can be opened by clicking the Curve Editor button in Sequencer.
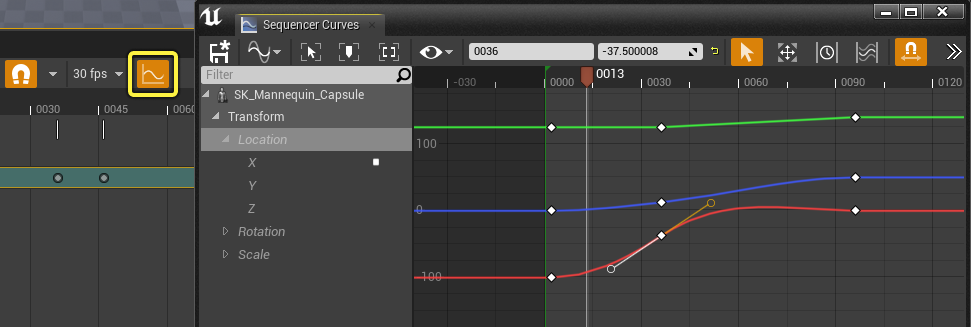
Visit the Curve Editor page for more information on the Curve Editor and its features.
Master Sequences, Shots, and Takes
To create robust cinematic sequences and to enable non-linear editing controls for your scenes, you can create Master Sequences which contain sub-sequences, known as Shots.
In a Master Sequence, you can edit, cut, and trim your Shots just like in any non-linear film editing tool. You can also specify Takes for your Shots which enable the adjustment of a Shot’s composition or animation while preserving the original Take.
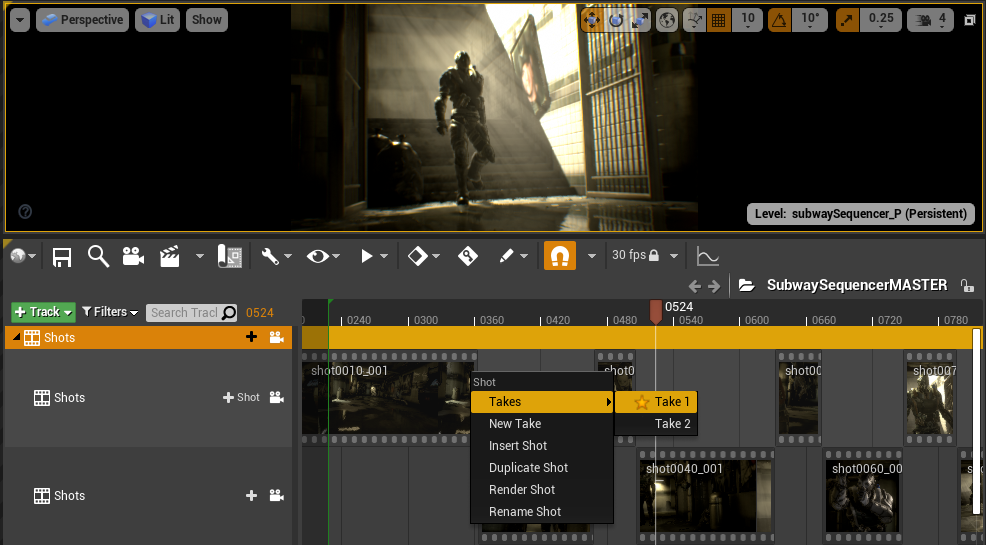
Visit the Master Sequences, Shots, and Takes page for more information.
Sequencer and Blueprints
Sequencer can interface with Blueprints to control playback of your sequences within gameplay. You can play, pause, stop, and jump to a particular time frame and you can even rebind tracks to other Actors in your Level.
Sequences can also be added within Blueprints using the Actor Sequence Component. This enables reuse of Sequences by binding the animations to the Blueprint instance and triggering them automatically or through the Event Graph.
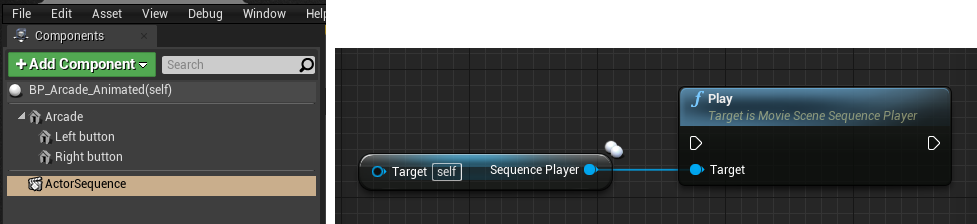
Visit the following pages for more information on how you can use sequences in your Blueprints.
Recording Sequences
Actors, animations, and other sources can be recorded directly into Unreal Engine using Take Recorder. Using Take Recorder and Live Link, motion capture data can be streamed and recorded to Sequencer tracks.
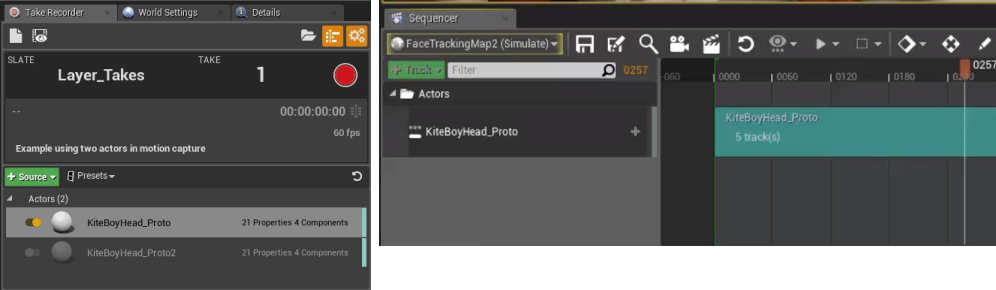
Visit the Take Recorder page for more information.
Sequencer Preferences
You can customize your Sequencer and cinematic experience in Unreal Engine by navigating to the Level Sequencer Editor section of Editor Preferences. Here you can adjust Sequencer preferences located under the Keyframing, Timeline, Snapping, Curve Editor, and Playback categories.
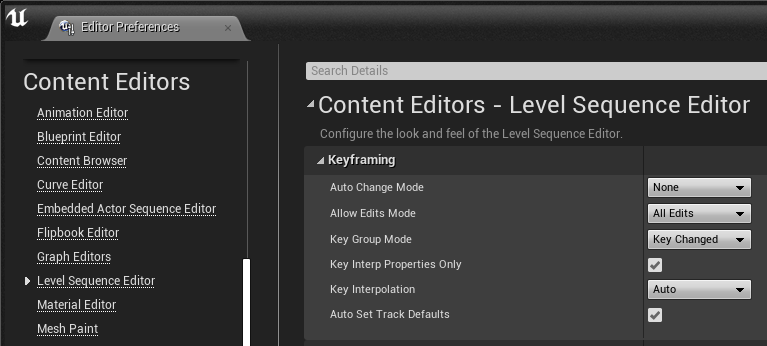
Visit the Editor Preferences and Project Settings page for a full list of Sequencer preferences and their effect.
Import and Export
Sequencer supports the ability to import and export your scene or Actors as an FBX file to other 3D software, such as Blender, 3ds Max, or Maya. Use these import and export workflows to edit your cinematic content in your preferred tools, and quickly bring it back into Unreal Engine.
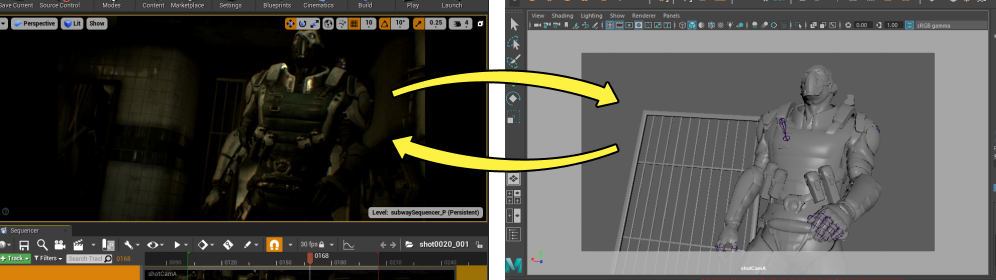
Visit the Importing and Exporting FBX files page for more information on these features.
Template Sequences
Template Sequences are a type of Sequence that supports the creation of reusable snippets of sequence data for individual Actors. Using this feature, you can layer and reference Actor sequence data from other sequences.
Visit the Template Sequences page for more information.
