Android File Server (AFS) is an Unreal Engine (UE) plugin that embeds a file server with your Android application when you package a Development, Debug, or Test project (or optionally a Shipping project, see below) build. As long as the file server is running, you can use the UnrealAndroidFileTool to manage, push, and view files. In builds that include AFS, Unreal Engine uses it for deploying Quick Launches. Together, AFS and UnrealAndroidFileTool are an alternative to using Android Debug Bridge (ADB), providing many of the same capabilities tailored to Unreal Engine's workflow.
Instead of using the device's SD card external storage for handling Quick Launches, AFS uses the package sandbox storage. This makes it possible to use file operations without requiring storage permissions or scoped access, which can be cumbersome to continually re-enable as you develop a project and deploy builds. AFS can also operate over WiFi connections, USB connections, or both for faster deployment.
Configuration and Setup
This section explains how to configure AFS's packaging and connections. You can find these settings in Project Settings > Plugins > AndroidFileServer. This section lists each of the available parameters to configure.

Packaging Settings
The Packaging section contains settings configuring what type of builds will include AFS and what capabilities the file server will have. AFS is enabled by default, and non-shipping builds will automatically embed a file server with your project unless it is disabled. AFS is not included in Shipping builds by default, but there are settings to enable it.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Use AndroidFileServer | If enabled, your project will include the embedded file server for packaged and Quick Launch builds. If disabled, AFS will not be used in your project, and Unreal Engine falls back to using ADB. |
| Allow Network Connection | If enabled, AFS allows WiFi connections and connections through USB. Refer to Connection Settings for more details. |
| Security Token | A unique string you can use to secure AFS and prevent it from being started remotely by anyone without the token. Refer to Using Security Tokens for more details. |
| Include in Shipping | If enabled, AFS will be included in Shipping builds. Refer to Using AFS in Shipping Builds for more details. |
| Allow External Start in Shipping | Paired with Include in Shipping, this allows external requests to start the file server with UnrealAndroidFileTool or for Quick Launch. |
| Compile AFSProject | If enabled, Unreal Engine will compile AFS as a separate APK when it packages your project. Refer to Compiling AFSProject for more information. |
Using AFS in Shipping Builds
Shipping builds do not normally include AFS, but you can enable Include in Shipping and Allow External Start in Shipping to add it. If you only enable Include in Shipping, you can still use AFS, but it won't be used for Quick Launches, and you will need to manually start and stop it from inside your application.
Starting and Stopping AFS
When using non-Shipping builds, or with External Start enabled for Shipping builds, a receiver is registered to allow remote start and stop of the file server. You can then use the UnrealAndroidFileTool to connect to your device's file server and manage files. Otherwise, with AFS enabled, you need to start the file server manually from inside your Unreal Engine application. Refer to Manually Starting and Stopping AFS with Blueprints for more information.
Using Security Tokens
If you fill in the Security Token field, your file server will require any incoming connection requests from UnrealAndroidFileTool to provide a matching Security Token. Refer to the UnrealAndroidFileTool reference for more information.
The Security Token offers only basic security, and is not encrypted in any way. You can use the Android File Server Blueprint library to provide more robust security of your own in Shipping builds. When using the Security Token, make sure not to give the token to anyone outside of your organization.
Compiling AFSProject and Installing AFS Manually
If Compile AFSProject is enabled, a standalone APK containing the file server will be packaged which matches your project's configuration and key signing. You may install this APK to the device to manage new or existing files with the adb install -r option. Afterwards, you may reinstall your actual APK with the same option without affecting the internal or external data files. This is especially useful if you need to manage files on a Shipping build that doesn't have the server built-in.
Shipping builds compile AFSProject regardless of whether Compile AFSProject is enabled.
Deployment Settings (Logging and Compression)
The settings in the Deployment section control what information the file server reports in your logs.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Use Compression (Beta) | Applies compression to data files on your file server. In UE 5.0, currently this has minimal impact on transfer time. |
| Log Files | Shows a list of files being pushed to the device. |
| Report Stats | Shows a listing of how many files are pushed to the device and the number of bytes pushed over your connection. |
When the log output settings are enabled, Unreal Engine logs information about AFS's installation process in the Console window during Quick Launches.
Logging With Both USB and Network Enabled
If USB and Network are both enabled, the AFS log will show a prefix denoting what type of connection the file was sent through.
| Prefix | Description |
|---|---|
| 1> | File was sent over USB. |
| 2> | File was sent over Wifi. |
For example, the following line indicates that a map file was sent through USB:
1> TestGameEntry.umap
If you are using both USB and WiFi, one connection will take over while the other is busy.
1> TestGameEntry.umap
2> TestTexture.uasset
2> TestMaterial.uasset
1> TestPawn.uasset
Connection Settings
The Connection section contains options for configuring what kind of connections AFS will use to connect your computer to a device.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | Determines whether to use USB, WiFi, or both to connect with your file server. |
| Use Manual IP Address | If enabled, the Quick Launch will use the Android device at the IP provided in the Manual IP Address field. Otherwise, it will try to discover the IP address over USB if connected. |
| Manual IP Address | The IP address of an Android device you want to connect to for Quick Launch. The device must be connected to your local WiFi network. |
Connection Types
The Connection Type dropdown selects what kind of connection to use to push files.
| Connection Type | Description |
|---|---|
| USB | Pushes files over a USB connection to your Android device. |
| WiFi Network | Pushes files over a WiFi connection to an Android device on the same local area WiFi network as your computer. This requires the Allow Network Connection setting to be enabled. |
| USB and Network Combined | Simultaneously uses a USB connection and a WiFi connection to push files. Whenever one connection is occupied transferring a file or a batch of files, the other will take over for the next file in the queue. This results in faster file transfers. This is integrated as part of the deployment process. |
Unless you override it, the default port for AFS is 57099.
Using a Manual IP Address
If you enable the Use Manual IP Address setting and provide an IP address for your Android device, when you deploy your build, AFS will connect to that device instead of the default device in the normal Device Manager workflow. The device must still be connected to the same WiFi network as your computer.
Manually Starting and Stopping AFS With Blueprints
You can use the Android File Server Blueprint library to manually start, stop, and check the status of your file server from inside your UE application.

| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Start File Server | Starts the file server using the designated Port for connections. You can choose whether to allow USB or Network connections when you use this node to start the server. The return value is a boolean indicating whether the server started successfully. |
| Stop File Server | Shuts down the file server if it is running. You can choose to close only specific connection types. The return value is a boolean indicating whether the server shut down successfully. |
| Is File Server Running | Returns the current status of the file server with
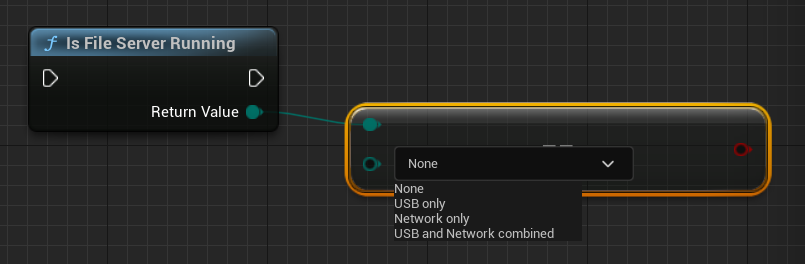
|
While AFS can provide basic security using a unique token generated for your project, these Blueprint nodes are useful for creating more secure ways to start and stop AFS compared with using the default broadcast receiver.
UnrealAndroidFileTool
UnrealAndroidFileTool is a command-line tool that can connect with the file server deployed on your device to manually manage files. You can find it in your engine's install directory under Engine/Binaries/DotNET/Android/UnrealAndroidFileTool. This directory includes folders for Linux, MacOS, and Windows versions of the executable.

If you need versions of UnrealAndroidFileTool executable for all three operating systems, open Project Settings > Platforms > Android and enable Generate Install Files for all platforms. If this setting is not enabled, Unreal Engine will only provide the executable that matches the editor host type in the packaged target directory.
When you run this executable through a command line, it will show a menu with all of its available functions. You can run the executable with any of these commands appended in your command line.

Command Reference
Commands for UnrealAndroidFileTool consist of a set of parameters telling the tool what to establish a connection with, followed by a command to send to the file server. For example, the following would run the shell command on a device with a specific serial number and look at the files for a specific project:
UnrealAndroidFileTool.exe -s AB187923123CD123 -p com.OrganizationName.ProjectName shell
Formatting Paths
Paths in AFS use the normal conventions for command line paths, but they also support several shortcuts for navigating the file hierarchy:
| Text | Description |
|---|---|
^^ |
Refers to the current base directory you set with the cd command. Refer to Query and Navigation Commands for more information. |
^-n |
Move up a specified number of directories, where n is the desired number. For example, ^-3 would move up three directories. This makes it easier to handle relative paths without using multiple instances of /.. |
^[key] |
Used at the start of a filepath to either act as a shortcut or query a given key, where [key] is replaced with the key's text. For instance, ^ext/ is the external package directory, and ^commandfile is a shortcut to the UECommandLine.txt file. See the table below for a list of useful shortcuts. |
The following are some common shortcuts using ^[key]. You do not have to use these, but they are convenient.
| Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|
| Shortcuts to Directories | |
^ext/ |
External storage directory. |
^int/ |
Internal storage directory. |
^storage/ |
External storage directory (requires READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE and/or WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE permissions). |
^obb/ |
The obb directory. |
^unreal/ |
The UnrealGame directory. |
^project/ |
The UnrealGame/[project] directory. |
^engine/ |
The UnrealGame/Engine directory. |
^game/ |
The UnrealGame/[project]/[project] directory. |
^saved/ |
The Saved directory. |
^logs/ |
The Logs directory. |
| Shortcuts to Specific Files | |
^commandfile |
The UECommandLine.txt file. |
^logfile |
The project log file. |
^mainobb |
The main .obb filepath. |
^patchobb |
The patch .obb filepath. |
| Non-filepath Queries | |
^packagename |
Package name of the project. |
^version |
Package version code. |
^ip |
IP address of the device on the network. |
Parameters
The following parameters can be placed before a file server command to configure your connection for specific target devices and projects.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
-s [device serial number] |
Sends the command to the device with the given serial number. |
-ip [IP address] |
Connects to a device with the given IP address. |
-t [port] |
Overrides the port used to connect to the device. If not otherwise specified, the default port will be 57099. |
-p [package name] |
The reverse-domain package name for the application you want to connect with. For example: com.OrganizationName.ProjectName. Package names are case-sensitive and must exactly match the string given in your project settings. |
-k [security token] |
Provides the security token needed to connect to the file server, as described under Using Security Tokens. |
Device Management Commands
The following table is a reference for the commands you can use to get information about available devices and recognized packages, or to stop remote servers.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
help [command] |
If you use the help command alongside the name of another command that has parameters, UnrealAndroidFileTool provides more information about that command and how to format it. |
devices |
Displays a list of connected devices that you can access. Devices with an @ prefix are authorized devices. Do not include the @ when providing a serial number with -s. |
packages |
Displays a list of packages with the AFS receiver enabled. |
stop-all [-w] |
Send a stop request to all packages with receivers. If you add -w, UnrealAndroidFileTool will wait for all listen binds to terminate before you can interact with it again. |
terminate |
Stops the designated remote server. |
Any command that interacts with a file server, such as push, pull, or shell, implicitly requests for it to start, so there are no commands for starting a server.
Interactive Mode Commands
You can use the following commands to enter and exit Interactive Mode. Interactive Mode functions similarly to ADB, opening a connection with the device and giving you a way to send multiple commands without having to run UnrealAndroidFileTool.exe for each command. UnrealAndroidFileTool will remain in Interactive Mode until you exit.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
shell |
Enters interactive mode. |
quit or exit |
Exit interactive mode. |
Query and Navigation Commands
The following commands fetch information about directories and files on your device, or provide navigation for your base directory during interactive mode.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
query [key] |
Show all variables with a specific key. |
getprop [key] |
Get the property associated with the given key. |
cd [path] |
Set the base directory. You can then use ^^ to refer to this directory instead of manually typing it out. |
pwd |
Show the current base directory. |
direxists [path] |
Outputs whether the directory at the provided path exists. |
ls [-l,-s,-R,-f] [path] |
Shows the contents of the directory at the provided path. The listed specifiers designate what information to output:
|
File Management
The following commands interact with or modify files on your device.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
mkdir [path] |
Create a directory at the given path. |
| ` rmdir [path]` | Delete a directory at the given path. |
fileexists [file] |
Outputs whether the named file exists. |
rm [file] |
Delete the named file. |
cp [source] [destination] |
Copies the [source] file to the given [destination] directory on the device. |
mv [source] [destination] |
Moves a [source] file to the given [destination] directory on your mobile device. |
pull [source] [destination] |
Copies a [source] file from your mobile device to the given [destination] directory on your PC. |
push [-c] [source] [destination] |
Copies a [source] file on your PC to the given [destination] directory on your mobile device. If you add the -c parameter, UnrealAndroidFileTool will compress the data. |
cat [file] |
Writes file contents from the device to the output log. |
deploy [-c] [file] |
Reads a text file with deployment source/destination pairs. If you add the -c parameter, UnrealAndroidFileTool will compress the files. |
Commandline File Commands
The following commands interact with or modify the UECommandLine.txt file for your project on your remote device.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
command [data] |
Writes data to the UECommandLine.txt file. If you provide no data, it will show the contents of the file. |
addcommand [data] |
Appends data to the UECommandLine.txt file. |
delcommand [data] |
Removes data from the UECommandLine.txt file. |
