Texturing functions provide for specialized handling of texture-based actions, such as adjusting UVs of a texture, cropping textures, and many others. The following is the list of Texturing Functions.
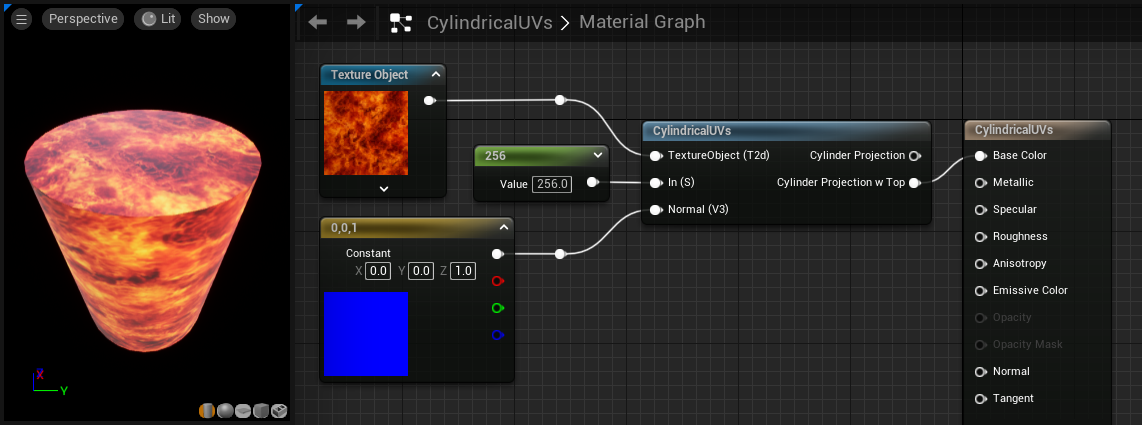
CylindricalUVs
This function tiles a texture around an object using cylindrically projected UVs centered around the object's center.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| TextureObject (Texture Object) | The texture to be projected via Cylindrical UVs. |
| In (Scalar) | This takes in the height of the projection cylinder in world space units. |
| Normal (Vector3) | Input a vector to rotate the projection cylinder. |
| Outputs | |
| Cylinder Projection | Outputs the resulting texture as if it was projected from a cylinder. There are no caps, however, so the texture will tend to pinch at the top and bottom. |
| Cylinder Projection w Top | Outputs the resulting texture as if it was projected from a cylinder, complete with caps. |
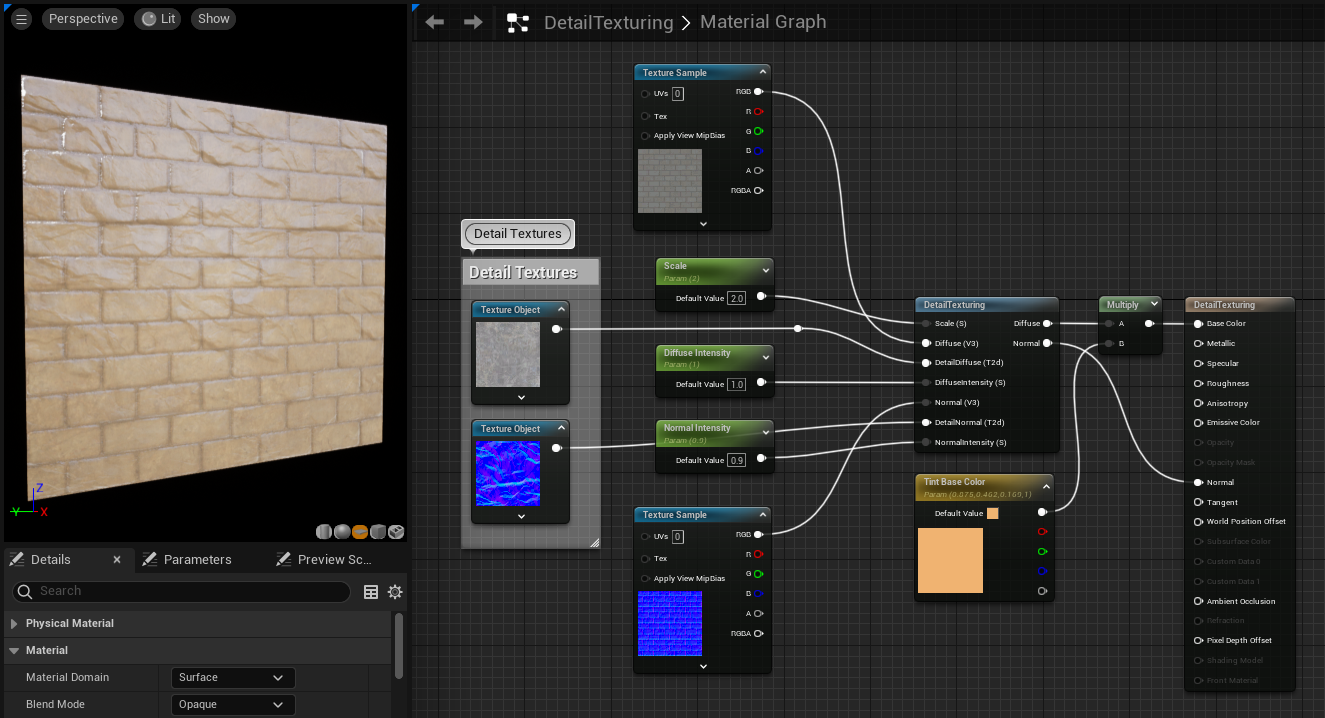
DetailTexturing
The DetailTexturing function simplifies the process of creating detail textures for your material. Detail texturing allows you to give the illusion of more detail in a texture by bringing in a more highly repeated diffuse and normal map combination which layers over the original diffuse and normal for an object. This gives the illusion of greater detail at close range.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| Scale (Scalar) | Controls the tiling of the detail normal and diffuse. |
| Diffuse (Vector3) | The original diffuse texture that requires more detail. |
| DetailDiffuse (Texture Object) | The diffuse texture for the added detail. |
| DiffuseIntensity (Scalar) | How much you want the detail diffuse to blend into the original diffuse. |
| Normal (Vector3) | The original normal which requires more detail. |
| DetailNormal (Texture Object) | The detail normal which will be used to add more detail to the original normal map. |
| NormalIntensity (Scalar) | How much the detail normal will show through over the original. |
| Outputs | |
| Diffuse | The result of the original diffuse texture blended with the detail diffuse texture. |
| Normal | The result of the original normal texture blended with the detail normal texture. |
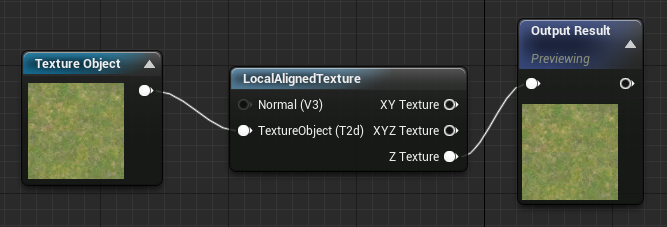
LocalAlignedTexture
The LocalAlignedTexture function tiles a texture on an object in local space.
Although this function has an input for a normal, at this time the input is nonfunctional.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| Normal (Vector3) | This takes in a normal to use as the object's surface reference. At this time, this input is nonfunctional. |
| TextureObject (Texture Object) | Takes in a texture to be tiled in world space. |
| Outputs | |
| XY Texture | The result of the texture as tiled across the world X and Y coordinates. |
| XYZ Texture | The result of the texture as tiled across the world X, Y, and Z coordinates. |
| Z Texture | The result of the texture as tiled across the world Z coordinate. |
ZWorldSpaceFlow
The ZWorldSpaceFlow function pushes a texture along the tangent space of an object, causing that texture to look like it is "flowing" along that surface. It works by making two variations of the texture panning in the same direction, but each with a slight offset from the other. It then blends each one over the other in a repeating fashion.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| FlowTexture (Texture Object) | This is the texture that you want to have flowing across the surface of your object. |
| FlowStrength (Scalar) | Controls the amount of blend that takes place as the two panning versions of the texture blend into one another. Fine tune this to control the surface area over which blending takes place. |
| FlowDirection (Vector2) | The 2D vector that controls the direction the texture will flow. |
| UVs (Vector2) | Any existing UVs for the texture to control tiling. |
| FlowSpeed (Scalar) | How fast the texture will flow across the surface. |
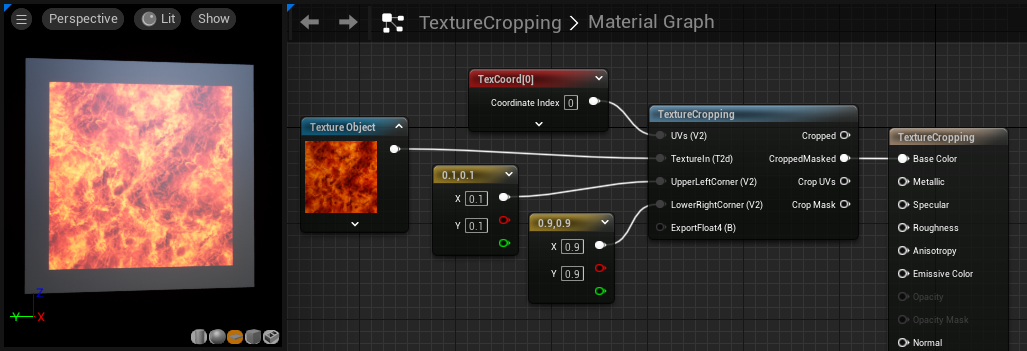
TextureCropping
The TextureCropping function allows you to crop down a given texture to a smaller and offset location on the texture coordinate plane. This is perfect for placing a block of color on top of an emissive texture region.
This function does not actually perform a true cropping operation such as one might be used to in image editing packages such as Photoshop. Rather, it remaps the existing texture to new coordinates in UV texture space, which is a lot more like scaling than cropping. However, the function is still highly useful for generating masks and adding color to texture regions.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| UVs (Vector2) | The texture coordinates used on the newly cropped texture. |
| TextureIn (Texture Object) | The texture that is to be cropped. |
| UpperLeftCorner (Vector2) | The location for the new upper-left corner of the texture in 0-1 texture space. |
| LowerRightCorner (Vector2) | The location for the new lower-right corner of the texture in 0-1 texture space. |
| Outputs | |
| Cropped | The result of the crop function. This will look a lot like a tiling operation. |
| CroppedMasked | This gives the result of the crop function, but while blacking out (masking) the areas outside the region defined by UpperLeftCorner and LowerRightCorner. |
| Crop UVs | The UV coordinates of the newly cropped region. |
| Crop Mask | A white area on a black background (mask) representing the area being cropped. |
WorldAlignedNormal
WorldAlignedNormal takes in a normal map and aligns its texture to the world, rather than locally to the object. It also allows for scaling in world units, rather than as a percentage of the texture size.
Because this function tiles the texture in world space, it is important to note that any animated objects textured in this manner will experience texture "swimming," in which the texture remains in place while the object slides underneath it.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| TextureObject (Texture Object) | This takes in the texture that will be tiled in world space. |
| TextureSize (Vector3) | The size of the texture in world units, along the X, Y, and Z axes. |
| Normal (Vector3) | This allows you to specify a normal direction for the world's up axis, thereby rotating the coordinates that this function uses. Defaults to 0,0,1, or Z-up. |
| WorldPosition (Vector3) | Provides an offset for the start point of the texture in 3D world space. |
| Outputs | |
| XY Texture | The result of the texture projected in world X and Y. |
| XYZ Texture | The result of the texture projected in world X, Y, and Z. |
| XYZFlatTop | The result of the texture projected in world X, Y, and Z, with an added contrast boost. |
| Z Texture | The result of the texture projected in world Z. |
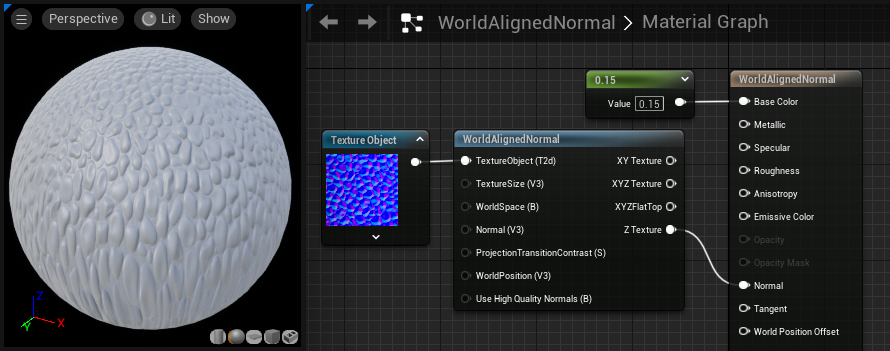
Notice the texture is still aligned to world coordinates, even though the floor is rotated.
WorldAlignedTexture
The WorldAlignedTexture function serves as a way to tile a texture across the surface of an object in world space, independently of that object's size or rotation. This function allows you to specify the direction in which the texture will be projected, and offers scaling in world units rather than as a percentage of the texture size.
Because this function tiles the texture in world space, it is important to note that any animated objects textured in this manner will experience texture "swimming," in which the texture remains in place while the object slides underneath it.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| TextureObject (Texture Object) | This takes in the texture that will be tiled in world space. |
| TextureSize (Vector3) | The size of the texture in world units, along the X, Y, and Z axes. |
| WorldPosition (Vector3) | Provides an offset for the start point of the texture in 3D world space. |
| ExportFloat 4 (StaticBool) | Whether or not to utilize the alpha channel of the incoming texture. Defaults to false. |
| World Space Normal (Vector3) | This allows you to specify a normal direction for the world's up axis, thereby rotating the coordinates that this function uses. Defaults to 0,0,1, or Z-up. |
| ProjectionTansitionContrast (Vector3) | When projecting in X, Y, and Z, this controls the contrast of the blend where two projection planes meet one another. |
| Outputs | |
| XY Texture | The result of the texture projected in world X and Y. |
| Z Texture | The result of the texture projected in world Z. |
| XYZ Texture | The result of the texture projected in world X, Y, and Z. |
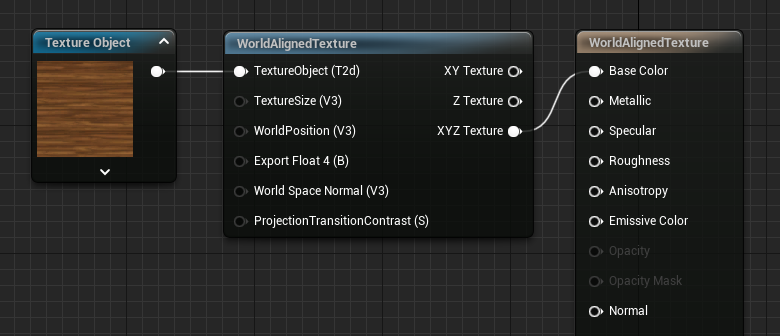
Notice the texture remains aligned to world coordinates, even when the plane is rotated.
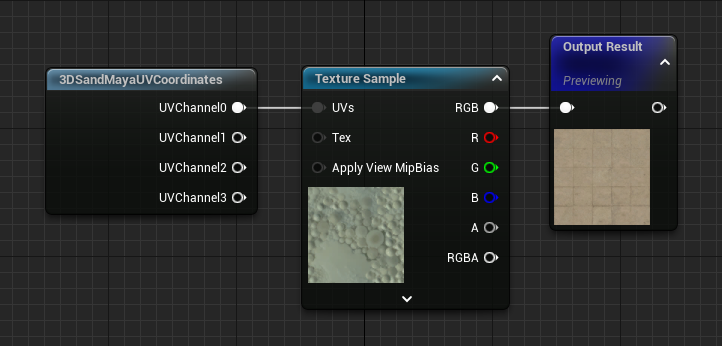
3DSandMayaUVCoordinates
This function flips the green channel of incoming UVs to place the 0,0 coordinate in the lower-left corner (as it is in 3ds Max and Maya) instead of the upper-left. This is important for models coming in from these applications, as it prevents you from having to flip textures.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Inputs |
-
UVChannel0 - V-flipped UVs from UV channel 0.
-
UVChannel0 - V-flipped UVs from UV channel 1.
-
UVChannel0 - V-flipped UVs from UV channel 2.
-
UVChannel0 - V-flipped UVs from UV channel 3.
CustomRotator
The CustomRotator function allows you to rotate a texture. However, it stands apart from the basic Rotator expression node in that it exposes a center point around which the image rotates. It also changes the rotation system to be 0-1 based, so that a value of 1 is considered a complete rotation, or 360 degrees. On a standard Rotator, a complete rotation requires a Time input of approximately 25.1.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| UVs (Vector2) | Takes in the existing coordinates for the texture. |
| Rotation Center (Vector2) | Location in texture space 0-1 that serves as the center of rotation. |
| Rotation Angle (0-1) (Scalar) | Rotation of the image in 0-1 format, with 1 being a full rotation. |
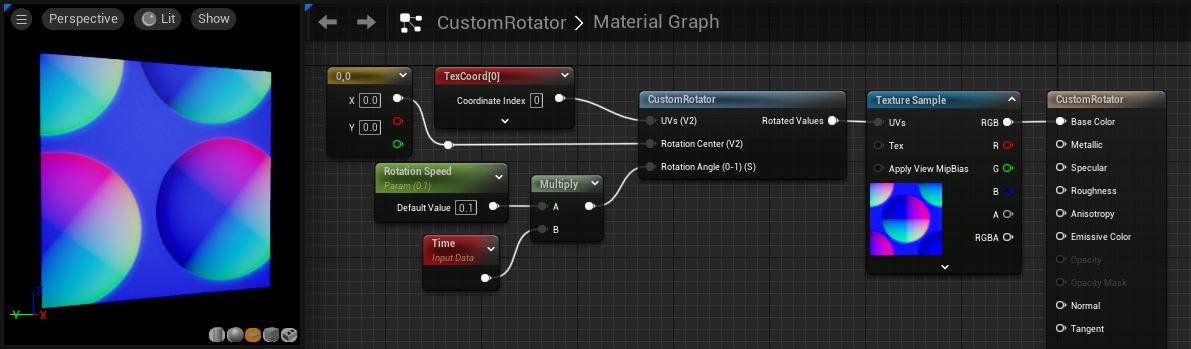
Note in the video how the center of rotation changes when the Rotation Center values are changed in the Material Graph.
HeightLerp
The HeightLerp function allows you perform a linear interpolation between 2 textures based on a heightmap and a transition phase value. This allows you to adjust the value along the hightmap that the lerp takes place.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| A (Vector3) | First texture of the lerp calculation. |
| B (Vector3) | Second texture of the lerp calculation. |
| Transition Phase (Scalar) | The value which defines the region of the heightmap where transition takes place. Leaving this at 0.5 performs a standard lerp, while adjusting the values toward 0 and 1 gives a bias toward the bottom or top of the heightmap, respectively. |
| Height Texture (Scalar) | The heightmap used for the lerp operation. |
| Contrast (Scalar) | Applies a contrast boost to the heightmap using the CheapContrast function. |
| Outputs | |
| Results | The blended result of the HeightLerp function. |
| Alpha | The alpha value used in the lerp, with contrast boosting applied. |
| Lerp Alpha No Contrast | The alpha value used in the lerp, without any contrast boosting applied. |
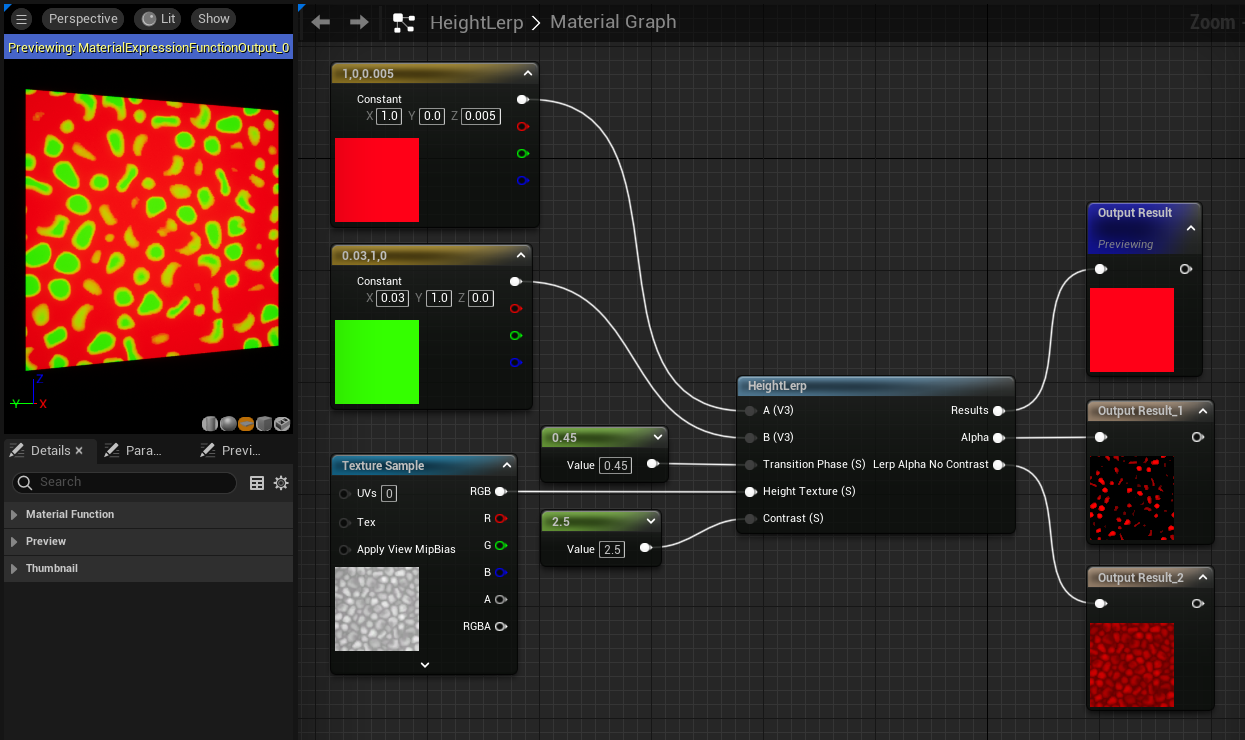
CameraWorldBlend
Outputs falloff results for the 3 primary world vectors based on the camera angle. Can be used to blend between textures based on direction the camera is looking.
This function appears to still be in development and may not give expected results.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| Blend Power (Scalar) | The rate at which the textures blend from one to the other. |
| Use Reflection Vector (StaticBool) | If true, uses ReflectionVector instead of CameraVector (Material's Normal input will affect results). This defaults to false. However, at this time, as there is no false input data for the switch, leaving this set to false will yield no result. |
| Use Smoothable Normals (StaticBool) | If true, uses ReflectionVector instead of CameraVector (Material's Normal input will affect results). This defaults to false. However, at this time, as there is no false input data for the switch, leaving this set to false will yield no result. |
| Smooth Reflection Percentage (Scalar) | How much to smooth the normals being applied to the surface prior to blend. |
| Outputs | |
| XY True | The falloff results which blend toward white as the surface aligns to the XY plane. |
| XZ True | The falloff results which blend toward white as the surface aligns to the XZ plane. |
| YZ True | The falloff results which blend toward white as the surface aligns to the YZ plane. |
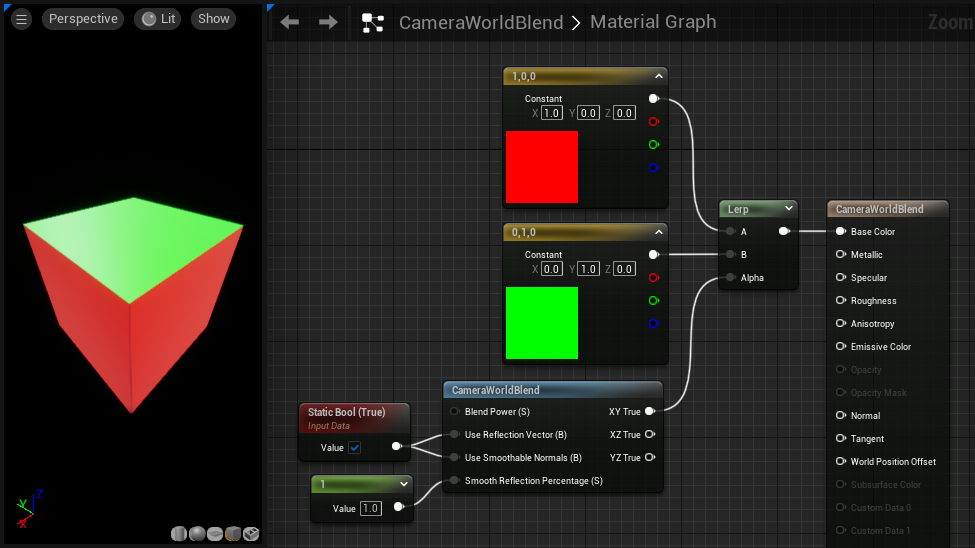
Notice that the green texture blends in wherever the surface aligns to the XY plane, with red everywhere else.
LocalSpaceSurfaceMirroring
The LocalSpaceSurfaceMirroring function applies mirroring to all faces of a surface that are oriented toward a given local axis. Other areas on the surface area masked out. These masks can be offset via a scalar input, and the entire calculation can be perturbed by a normal map. This is useful when you need to produce mirroring based on a surface's topology.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| Use NormalMap (StaticBool) | Sets whether to calculate the direction of the surface after applying a normal map. |
| Normal Map (Vector 3) | Takes in a normal map that is used to perturb the object's surface prior to the local topology calculation. |
| In (Scalar) | This is an offset value that moves the resulting mask around. |
| Outputs | |
| Local X | Outputs a masked mirror effect that only affects those surfaces facing the local X axis. |
| Local Y | Outputs a masked mirror effect that only affects those surfaces facing the local Y axis. |
| Local Z | Outputs a masked mirror effect that only affects those surfaces facing the local Z axis. |
SubUV_Function
SubUV_Function is perfect for handling animation across a sprite sheet or texture with multiple frames. The function takes in a texture object, and based on the outputs can show a blended-frame animation of the frames on that texture.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| Texture (Texture Object) | The incoming sprite sheet texture. |
| UVs (Vector2) | The UV coordinates for the texture, in case any tiling is needed. |
| SubImages (Vector2) | The number of frames on the texture, horizontally and vertically. |
| Frame (Scalar) | The current frame of the animation. This is zero-based and will blend on decimal values. For instance, a value of 2.35 would produce a 35% blend between the third and fourth frame. |
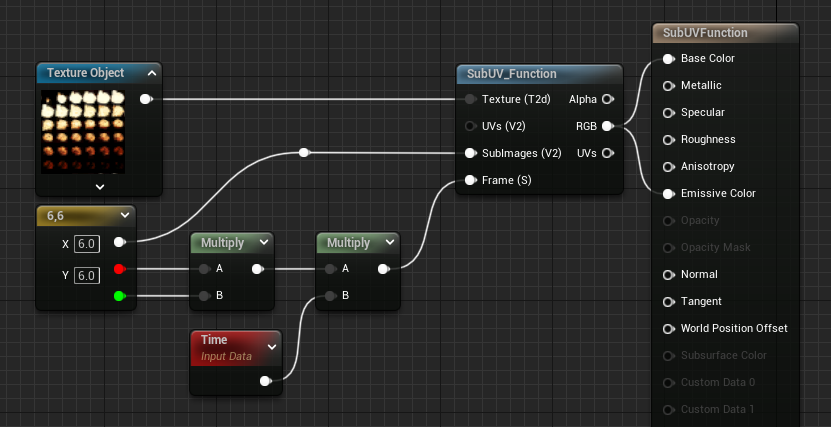
TwoSidedTexturing
The TwoSidedTexturing function provides individual texture inputs for both sides of a two-sided material. This function does nothing if the material's Two Sided property is not active.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| Texture Side A (Vector3) | The texture used on the positive side (outside) of the polygons. |
| Texture Side B (Vector3) | The texture used on the negative side (inside) of the polygons. |
| Use Surface Normals (StaticBool) | Tells the shader whether it should be using an incoming normal map to aid in calculating positive and negative sides of the mesh. |
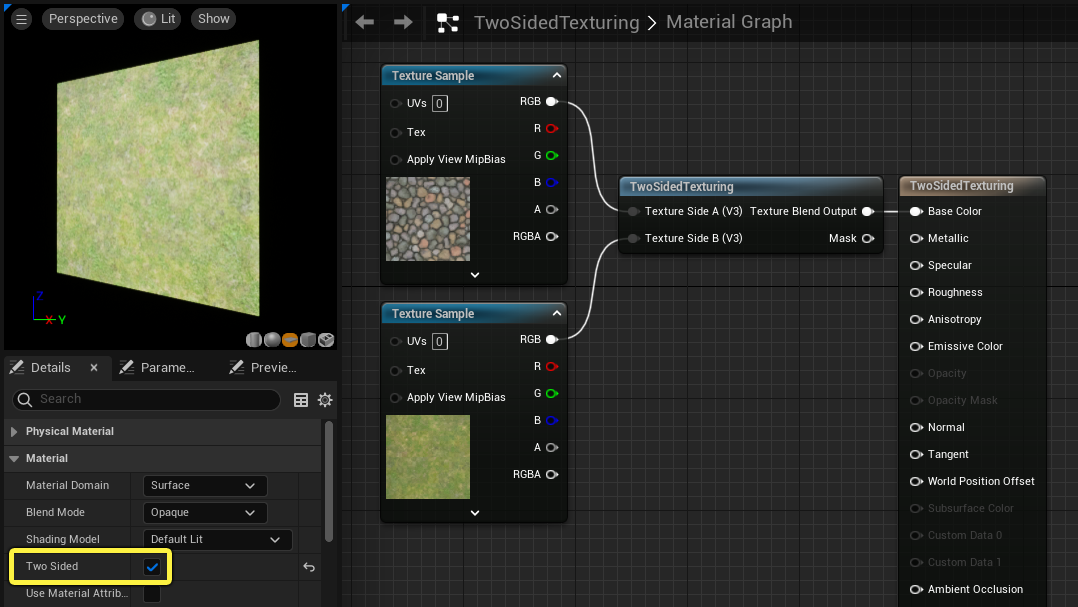
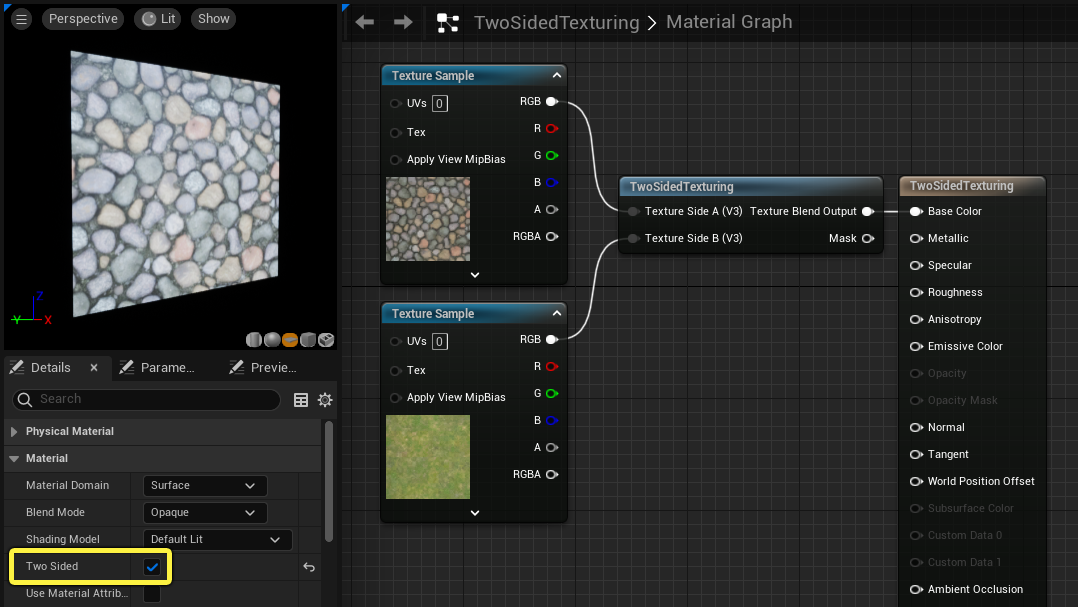
A different texture is applied to each side of the plane.
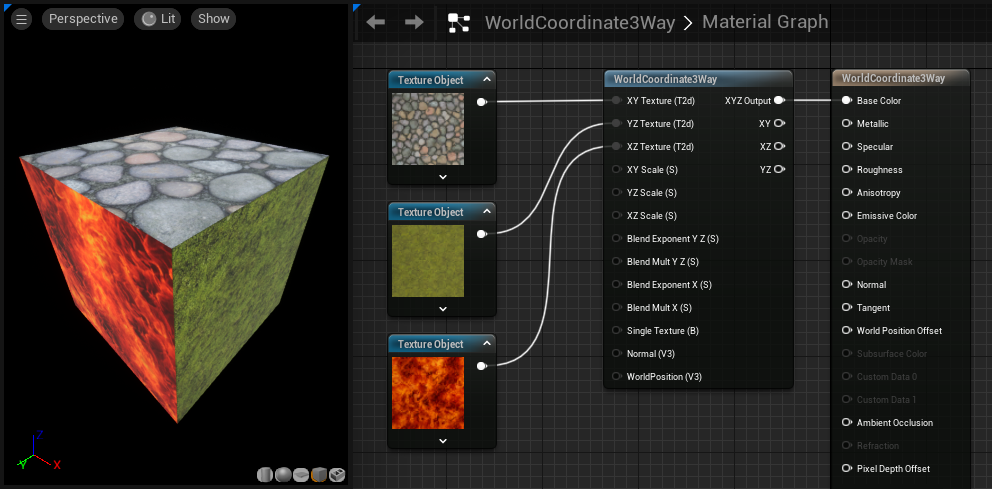
WorldCoordinate3Way
The WorldCoordinate3Way function projects a texture onto the surface of an object in world coordinates. The user has control over how multiple textures blend together at the edges, and a normal map can be added to perturb the surface prior to the calculation.
Because these textures are projected along world coordinates, any motion or rotation of the given object will cause the textures to "swim" along the surface.
| Inputs | Description |
|---|---|
| XY Texture (Texture Object) | The texture that will be projected onto the XY plane. |
| YZ Texture (Texture Object) | The texture that will be projected onto the YZ plane. |
| XZ Texture (Texture Object) | The texture that will be projected onto the XZ plane. |
| XY Scale (Scalar) | Scaling applied to the texture that is being projected onto the XY plane. |
| YZ Scale (Scalar) | Scaling applied to the texture that is being projected onto the YZ plane. |
| XZ Scale (Scalar) | Scaling applied to the texture that is being projected onto the XZ plane. |
| Blend Exponent Y Z (Scalar) | Controls the rate of transition between the textures being projected along Y and Z. |
| Blend Mult Y Z (Scalar) | Multiplies the blend between the sides. |
| Blend Exponent X (Scalar) | Controls the rate of transition between the textures being projected along X. |
| Blend Mult X (Scalar) | Multiplies the blend between the sides. |
| Single Texture (StaticBool) | When set to true, this uses only the texture applied to the XY Texture input and projects it on all 3 sides. |
| Normal (Vector3) | This brings a normal map into the blend calculation, using it to determine what direction the surface is facing. |
| WorldPosition (Vector3) | This optional output allows you to offset the location of the projection center. |
| Outputs | |
| XYZ Output | Outputs all 3 textures, projected from each plane, blending them at the edges. |
| XY | Outputs only the texture being projected along the XY plane. |
| XZ | Outputs only the texture being projected along the XZ plane. |
| YZ | Outputs only the texture being projected along the YZ plane. |