This page outlines the interface elements and options contained within the Remote Control Panel. You will learn how to organize the Remote Control Panel, connect external devices, and rename elements for simpler reference in the Remote Control API.
Remote Control Panel Interface
Click image to expand
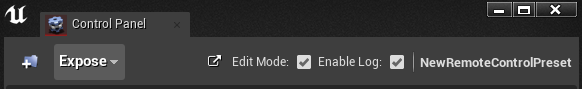
Menu
The following table describes each element as it appears in the Menu, from left to right.
| UI Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Create Group | Create multiple groups to organize similar properties and functions together. |
| Expose | Add other items to the panel where you want to expose functionality that is not merely a property. The following options are available to expose to the Remote Control API:
|
| Open Web App | Launches the Remote Control Web Application in your browser. |
| Edit Mode | When enabled, you can expose properties from the Editor, add functions to the Preset, and modify the groups and positions of the properties and functions. |
| Enable Log | Shows the Protocol Log. See the Protocol Log section for more details. |
| Remote Control Preset Name | Displays the name of the Remote Control Preset Asset that’s currently open. |
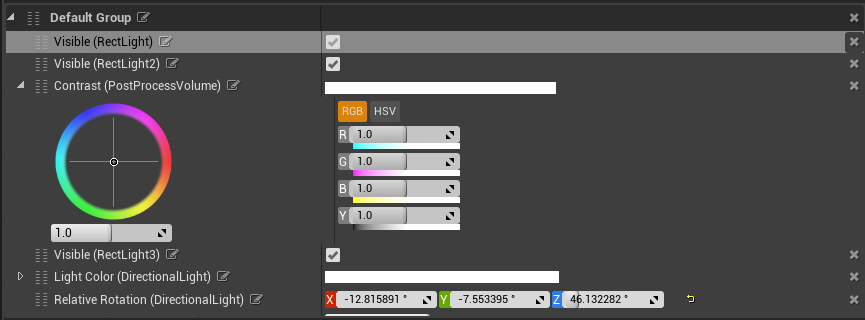
Exposed Properties
The following table describes each element as it appears for each exposed property, from left to right.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Expand | (Optional) Shows additional information for the data value, if it exists. |
| Move | Rearrange properties, functions, and groups by dragging and dropping the elements in the panel. |
| Rename | Change the names of the properties, functions, or groups to make their references clearer and simpler in function calls. |
| Data Values | Matches the data format for the property in the Editor. |
| Reset | Return the property's value back to its default value. |
| Remove | Remove the property or function from the Panel and make it no longer exposed to the Remote Control API. |
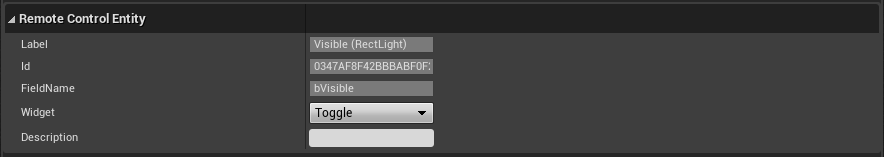
Remote Control Entity
This section appears when you select an exposed property. The following table describes the Metadata that you can associate with each property. Some of the properties might have more fields depending on their data format.
| Metadata | Description |
|---|---|
| Label | The unique label for the property that matches the label in the Remote Control Preset. This can be used in the Remote Control API to access an exposed property. |
| ID | The engine’s unique identifier for the property. This can be used in the Remote Control API to access an exposed property. |
| FieldName | The name of the associated field. |
| Widget | The default widget type to use for this property in the Remote Control Web Application. |
| Description | This field overrides the label that is displayed in the Remote Control Web Application. |
Remote Control Protocols for DMX, MIDI, and OSC
(#remotecontrolplugins)
In the Remote Control Panel, you can map exposed properties to an external device through DMX, MIDI, and OSC. The table below describes the UI for adding and viewing Protocol Mappings.
| UI Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol Mapping Option | Options include:
|
| Add Protocol | Creates a new Protocol Mapping for the currently selected option in the Protocol Mapping Option dropdown. |
| Viewing Options | Filter which protocol mappings you want to view. |
Each Protocol Mapping also has its own Mapping and Ranges sections to define which external device and input to connect to. The sections below explain the differences between mappings for Protocol types, and the functionality of ranges shared between the Protocol types.
Use the autobinding button to capture the latest input for the current protocol and apply it to the mapping. This provides a convenient and faster alternative to specifying the properties manually.
For example, in either an existing or newly created MIDI binding, you can toggle autobinding, press a note on the device, and the mapping properties will be populated accordingly. To complete the autobinding and stop recording to any new input, toggle the autobinding button again so that it's no longer red.
The following are the available states for autobinding: Grey: Not listening for input Red: Listening for input * Green: With a bound input
DMX Protocol Mapping
The following table describes the options for connecting to a specific input on an external device with the DMX Protocol.
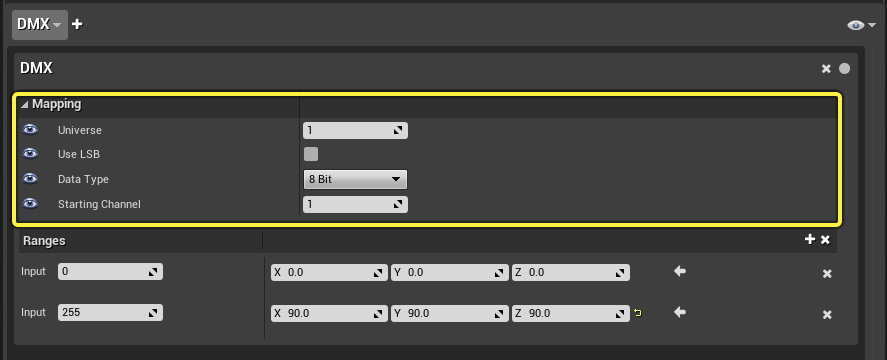
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Universe | DMX Universe Mapping |
| Use LSB | When enabled, uses the least significant bit to swap the byte order, if the order is not standard when using 16-bit DMX values. Typically, the most significant bit is used. |
| Data Type | Specifies the precision and max value of the incoming data. Input will be clamped to the bounds of this type. Available types are:
Currently, the 24 bit option is stored internally and represented as a 32-bit integer. |
| Starting Channel | The first channel of DMX to which you are binding the property. Currently, only one channel is allowed to be bound to a parameter. |
MIDI Protocol Mapping
The following table describes the options for connecting to a specific input on an external device with the MIDI Protocol.
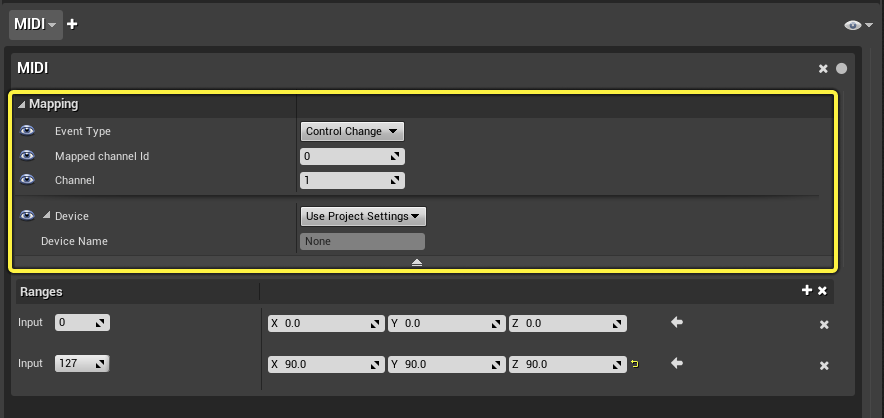
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Event Type | Specifies the type of Input Event. The default type is Control Change. The following are the available types:
|
| Mapped Channel ID | Specifies which device to connect to using the MIDI device input identifier. |
| Channel | Input MIDI channel. Expected range of values are 0-16. |
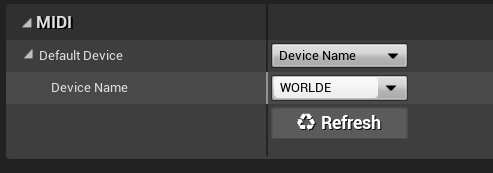
| Device | Selects which device to map. Default is to use what’s set in Project Settings. You can also override the device per protocol binding by setting the device by its Name or ID. |
To specify the MIDI device in the Project Settings:
- In the Editor, go to the main menu and select Project Settings to open the Project Settings window.
- In the Project Settings window, navigate to Plugins > Remote Control MIDI Protocol.
- Select the device by its Name or ID. The dropdown next to either field shows a list of available devices, or you can specify your device if it isn’t currently connected.
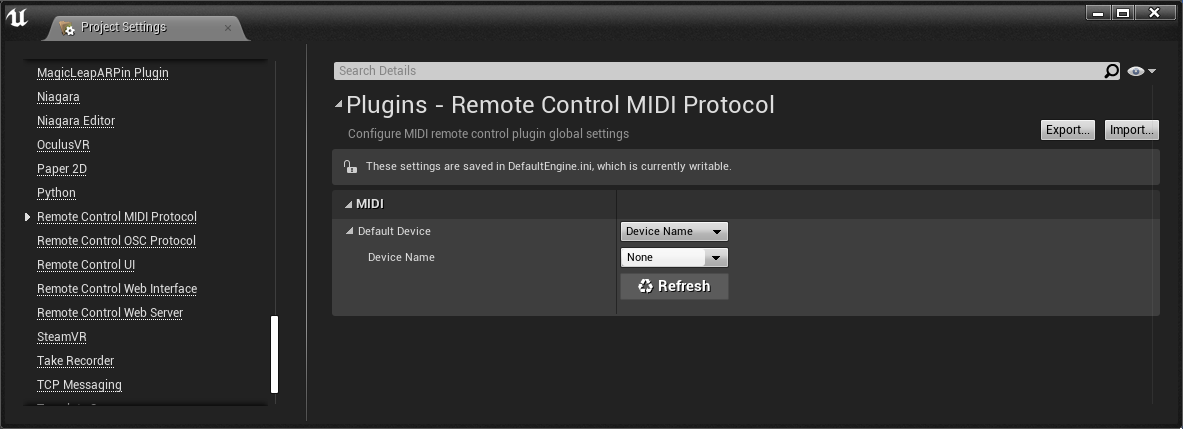
If you plug a device in while the Editor is open, you can refresh the device list by clicking the Refresh button.
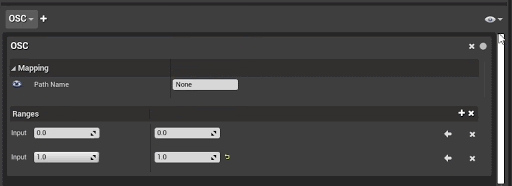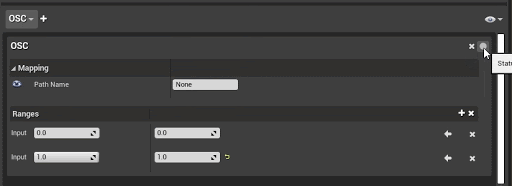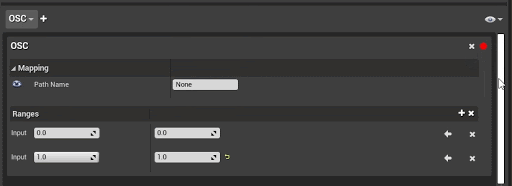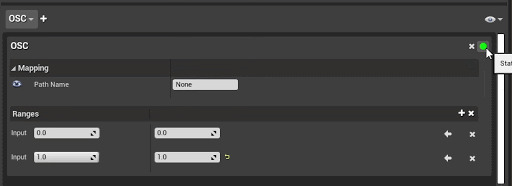
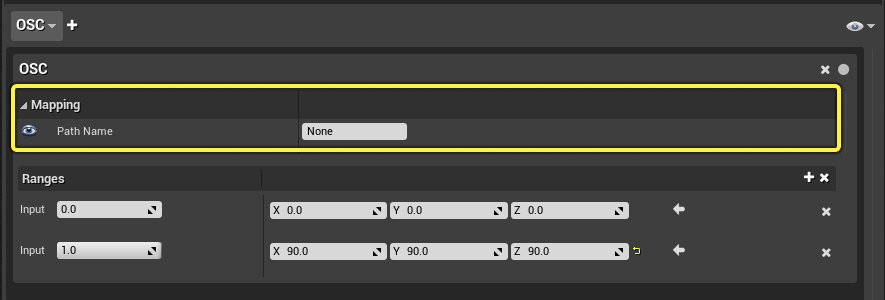
OSC Protocol Mapping
The following table describes the options for connecting to a specific input on an external device with the OSC Protocol.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Path Name | Specify the server address and path for the OSC device. |
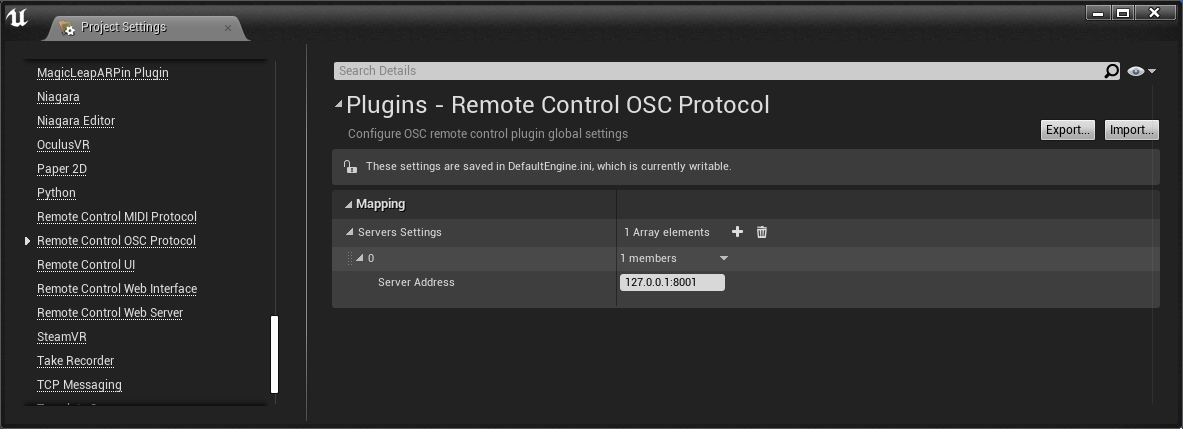
By default, the server is 127.0.0.1:8001. You can change or add more options in Project Settings:
- In the Editor, go to the main menu and select Project Settings to open the Project Settings window.
- In the Project Settings window, navigate to Plugins > Remote Control OSC Protocol.
- Add a new Server Settings array element or modify an existing one, and set its Server Address to match your device.
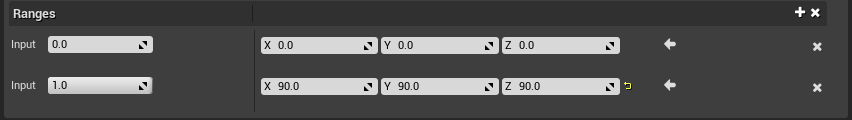
Protocol Ranges
This section displays the ranges mapped to the external device. By default, a new protocol mapping adds two range inputs, corresponding to the predicted min and max values.
You can add more range steps by selecting the plus button to the right of the ranges section. If you enter different values for the range points, the property value will interpolate between the input points, like keyframes in animation.
The following table describes how to set property values for the ranges.
| UI Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Range Point | The input point with which you can associate a specific property value. |
| Data Values | Sets the value of the property for that range point. The data format matches the associated property’s type. |
| Use Current Property Value | Captures the current value of the property in the level. |
| Remove Input | Removes the range point. |
A warning icon appears when you have more than one mapping for the same input on an external device.
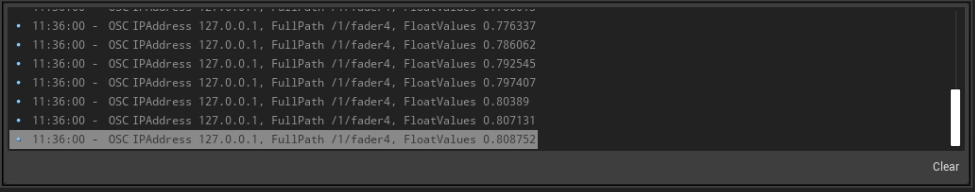
Protocol Log
When Enable Log is checked in the Remote Control Panel’s Menu, this section will show incoming data for the selected Protocol. In the example below, an OSC device with the name /1/fader4 is sending float values to the engine.