Quartz is a Blueprint-exposed scheduling system that solves timing issues between the game, audio logic, and audio rendering threads to provide sample-accurate audio playback.
Quartz has many applications. For example, you can use Quartz to:
- Create dynamic music systems.
- Control playback of timing-dependent sound effects, such as automatic weapon fire.
Latency: The Problem Quartz Solves
Unreal Audio Engine renders audio samples in buffers, which are sent individually to output hardware, known as a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). These buffers typically contain hundreds or even thousands of samples at a time.
Audio rendering commands, such as playing a sound or changing a sound's parameters, are typically consumed at the beginning of an audio buffer render. Because of this, the size of the rendered buffer controls the rate at which new commands are consumed and causes perceivable latency on any issued commands.
For example, if you trigger an explosion visual effect and an explosion sound effect on the same game thread tick, the latency between the visual and sound is determined by the buffer size. If that buffer contains 2048 samples rendered at 48k samples per second (kHz), the buffer results in an audible latency of up to 43 milliseconds (ms).
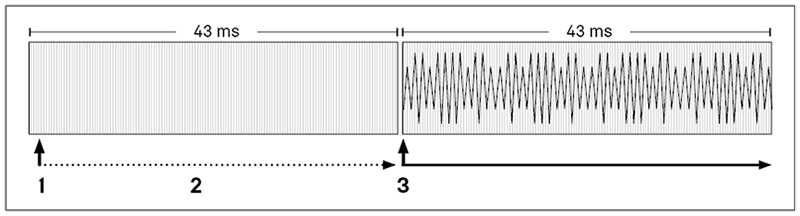
If a play command is issued after a buffer starts rendering (1), the command carries forward without playing (2) until the beginning of the next buffer (3).
Additionally, commands issued from the game thread take time to get to the audio engine. In the previous example, if the threading latency was 13 ms and the command just missed the start of the buffer render, the worst-case latency would be 56 ms.
To further complicate matters, game thread ticks are highly variable, decoupled from audio thread timings, and susceptible to hitches during garbage collection, asset loading, and so on.
These latency issues are not significant for some audio applications. Depending on CPU load or platform constraints, you might be able to tweak buffer sizes and counts to make the latency imperceptible.
How Quartz Works
Instead of rendering at the beginning of an audio buffer, Quartz schedules rendering on a time value (seconds) or a musical value (bars or beats) independent of buffer size, game thread timing, or other sources of variable latency.
By scheduling ahead of time, Quartz accounts for latency so sounds can render with sample-level accuracy without delay.
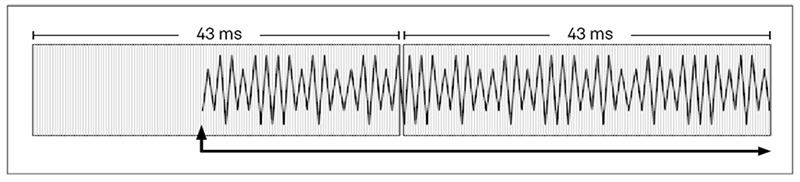
Quartz provides sample accuracy. You can schedule a command mid-buffer instead of delaying the audio render until the beginning of the next buffer.
Inter-thread Communication Flow
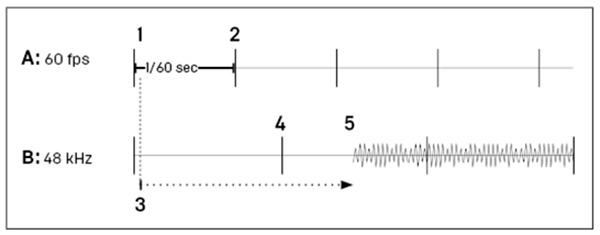
In the diagram above, A represents the game thread with game frame tick divisions, and B represents the audio render thread with buffer divisions.
The inter-thread communication flow proceeds as follows:
- The game thread requests Quartz play a sound on a given quantization boundary.
- Quartz issues the request and queues the rendering in the future.
- The request is held for a computed amount of time.
- This request may even be held beyond the beginning of the buffer.
- The request is then rendered on the given quantization boundary.
Quartz Key Concepts
Quartz Clock (Object)
The Quartz Clock is responsible for scheduling and triggering events on the audio rendering thread. You create a Quartz Clock with the Quartz Subsystem and modify it using Quartz Clock Handles. Each Quartz Clock has a Quartz Metronome.
Quartz Metronome (Object)
The Quartz Metronome is an object on the audio render thread that tracks the passage of time and schedules future commands based on settings like time signature and beats per minute (BPM).
Quartz Clock Handle (Object)
The Quartz Clock Handle is a proxy on the game thread used to control the Quartz Clock running in the audio renderer. You can access the Quartz Clock Handle from the Quartz Subsystem.
Quartz Subsystem (Object)
The Quartz Subsystem provides access to general system functionality that does not relate to a specific clock, including creating clocks, verifying clock existence, and querying latency information.
Play Quantized (Function)
Play Quantized is a function that takes an Audio Component input and plays the sound on a given clock with specified timing.
When calling Play Quantized, you can set an input delegate to synchronize with the quantized audio.
Subscribe to Quantization Event (Function)
Subscribe to Quantization Event is a function that takes a Quartz Clock Handle and notifies a given input delegate on a specified quantization event, such as every beat.
The Subscribe to All Quantization Events variant triggers on every quantization event. When using this variant, you can use a Switch node on the Quantization Type to build your logic on multiple timings.
