You can assign metadata to any Asset in your Unreal Engine Project, to record information about that specific Asset that you might need to make use of later on. This metadata is a set of key-value pairs that you can define freely for your own purposes.
For example, metadata could include things like the name of the Asset's creator, the intended usage of the Asset in your Project, or the status of the Asset in your team's workflow (like In Progress, Done, Approved, and so on).
Once set, you can use this metadata to help filter Assets in the Content Browser, or to identify Assets in Blueprint or Python scripts that you run in the Unreal Editor.
Because this metadata is assigned to the Assets in your Project, you can't access it directly in your runtime gameplay code. It is intended primarily for scripting Asset management operations in the Unreal Editor.
You can also import metadata that you've created in some third-party applications into Unreal Editor along with your Assets. For details on how to get metadata into the Unreal Engine through the FBX import process, see FBX Asset Metadata Pipeline.
Using Metadata in the Unreal Editor UI
Although you can't currently modify metadata in the UI Unreal Editor, you can view the metadata attached to any Asset, and you can use metadata keys to filter the Assets shown in your Content Browser.
Viewing Metadata on Assets
To view the metadata assigned to any Asset, right-click the Asset in the Content Browser, and choose Asset Actions > Show Metadata.
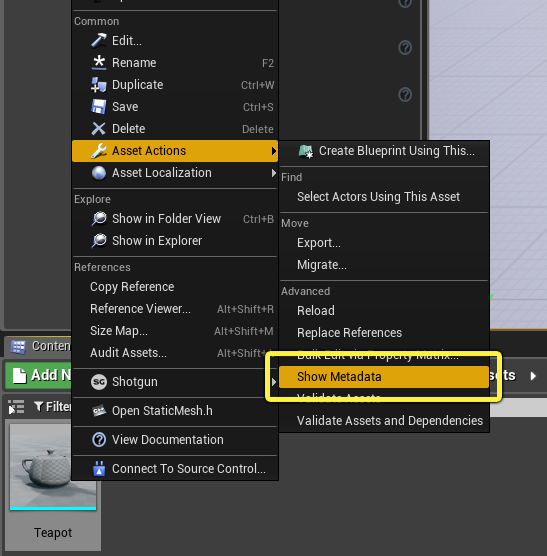
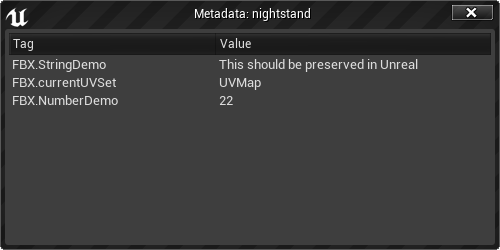
You'll see a list of all the keys and values attached to that Asset:
Filtering the Content Browser
To filter the Assets in the Content Browser by specific metadata tags:
-
Open the Project Settings window by choosing Edit > Project Settings from the main menu.
-
Select the Game > Asset Manager section, and find the Asset Registry > Metadata Tags For Asset Registry setting. Add to this list the names of any keys you want to be able to use for filtering Assets.
Click for full image.
-
In the Filters bar of the Content Browser, type the tag name followed by
=, followed by the value you want to search for. The list of Assets is automatically filtered to only show Assets that contain the metadata tag you specify, and for whom the value of that tag matches the value you type after the=.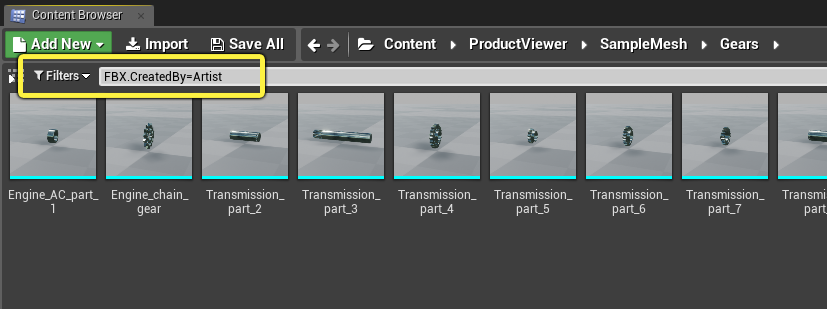
Working with Asset Metadata
You'll need to install the Editor Scripting Utilities plugin if you haven't already. For details, see Scripting and Automating the Editor.
You'll find the nodes you'll need to manage Asset metadata under the Editor Scripting > Metadata category.
To use these nodes, your Blueprint class must be derived from an Editor-only class, such as the PlacedEditorUtilityBase class. For details, see Scripting the Editor using Blueprints.
- The Asset you want to work with has to be loaded before you can work with its metadata. You can use the Editor Scripting > Load Asset node to do that. If you set or remove metadata values, you'll also need to use a node like Save Asset or Save Loaded Asset afterward if you want to keep your changes.
Getting Metadata from an Asset
-
If you know the name of the metadata key you want to retrieve, you can use the Get Metadata Tag node. For example, this script retrieves the value of a single tag by name, and prints it to the Viewport:
Click for full image.
-
You can also use the Get Metadata Tag Values node to retrieve all of the metadata as a map of tag-value pairs. For example, this script retrieves all metadata for an Asset, and writes each key and each value to the Viewport in order:
Setting New Metadata Tags
Use the Set Metadata Tag node. For example:
Click for full image.
If the tag name you specify does not already exist in the Asset's metadata, it is added with the value you specify. If the Asset already has a tag with the name you specify, the value of that tag is updated.
Removing Existing Metadata
Use the Remove Metadata Tag node, and provide the tag name you want to remove. For example:
Click for full image.
If you want to remove all metadata tags from an Asset, you can call this node in a loop:
Click for full image.
You'll find the functions you need for managing metadata in the unreal.EditorAssetLibrary class.
- The Asset you want to work with has to be loaded before you can work with its metadata. You can use
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.load_asset()to load the Asset from its filename in your Project content. If you set or remove metadata values, you'll also need to use a function likeunreal.EditorAssetLibrary.save_asset()orunreal.EditorAssetLibrary.save_loaded_asset()afterward if you want to keep your changes.
Getting Metadata from Assets
-
If you know the name of the metadata key you want to retrieve, you can use the
get_metadata_tag(asset, tag_name)function. For example, this script retrieves the value of a single tag by name, and prints it to the log:import unreal asset_name = "/Game/ProductViewer/SampleMesh/Gears/Transmission_part_10" tag_name = "CreatedBy" loaded_asset = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.load_asset(asset_name) value = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.get_metadata_tag(loaded_asset, tag_name) if not value is "": unreal.log("Value of tag " + tag_name + " for asset " + asset_name + ": " + value) -
You can also use the
get_metadata_tag_values(asset)function to retrieve all of the metadata assigned to an Asset as a dictionary. You can then loop through the keys and values. For example, this script retrieves all metadata for an Asset, and writes each key and each value to the log in order. Note that the keys in this dictionary are not actually strings, butunreal.Nameobjects. You can coerce these objects to strings using the built-instr()function.import unreal asset_name = "/Game/ProductViewer/SampleMesh/Gears/Transmission_part_10" loaded_asset = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.load_asset(asset_name) all_metadata = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.get_metadata_tag_values(loaded_asset) for tag_name, value in all_metadata.iteritems(): if not value is "": unreal.log("Value of tag " + str(tag_name) + " for asset " + asset_name + ": " + value)
Setting New Metadata Tags
Use the set_metadata_tag(asset, tag_name, value) function. For example:
import unreal
asset_name = "/Game/ProductViewer/SampleMesh/Gears/Transmission_part_10"
tag_name = "CreatedBy"
value_to_set = "My Name"
loaded_asset = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.load_asset(asset_name)
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.set_metadata_tag(loaded_asset, tag_name, value_to_set)
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.save_asset(asset_name)
If the tag name you specify does not already exist in the Asset's metadata, it is added with the value you specify. If the Asset already has a tag with the name you specify, the value of that tag is updated.
Removing existing metadata tags
Use the remove_metadata_tag(asset, tag_name) function, and provide the name of the tag you want to remove. For example:
import unreal
asset_name = "/Game/ProductViewer/SampleMesh/Gears/Transmission_part_10"
tag_name = "CreatedBy"
loaded_asset = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.load_asset(asset_name)
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.remove_metadata_tag(loaded_asset, tag_name)
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.save_asset(asset_name)
If you want to remove all metadata tags from an Asset, you can call this function in a loop:
import unreal
asset_name = "/Game/ProductViewer/SampleMesh/Gears/Transmission_part_10"
tag_name = "CreatedBy"
loaded_asset = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.load_asset(asset_name)
all_metadata = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.get_metadata_tag_values(loaded_asset)
for tag_name in all_metadata:
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.remove_metadata_tag(loaded_asset, tag_name)
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.save_asset(asset_name)
